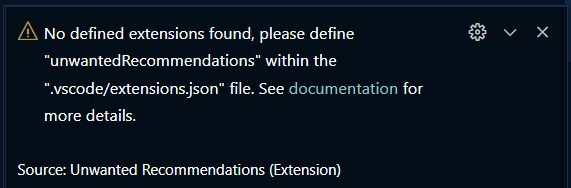
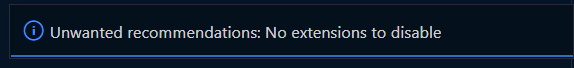
This extensions notifies developers about extensions which are not recommended for a specific workspaces.
For example: You want to tell your team mates, that a specific package or version of an extension should be disabled.
Because of VSCode limitations, it's not possible to do it automatically, but we instead show a warning and lead the developer to the mentioned extensions, whenever he opens a project.
More details can be read in this 👀 blog post.
Unwanted extensions is the continuation of the previous extension Unwanted Recommendations which is not maintained anymore. It's just a new publisher, still the same maintainer.
The VSCode Team introduced profiles, which went into a good direction and might be the solution in the future for that. But still, there seems to be issues or unsupported details, like
- Deprecating specific extensions for a workspace
- Also handling SemVer with extensions is a topic
Until then, it's not easy to handle it. This extension tries to improve the experience for developers.
This extension allows you to put unwanted extensions, into the already existing .vscode/extensions.json file, which already seems to kind of support the property unwantedRecommendations. Simply put your vscode extension id's in this array.
Following is a possible example for using Volar, and check for disabled Vetur, Typescript Vue Plugin amd (@builtin) Typescript Language Features:
{
"recommendations": [
"vue.volar"
],
"unwantedRecommendations": [
"vscode.typescript-language-features",
"octref.vetur",
"vue.vscode-typescript-vue-plugin"
]
}Note: This extension is only handling the
unwantedRecommendations, as therecommendationsare already handled by VSCode.
If you want to mark a specific version or range of versions as deprecated for your workspace, you can now add the unwanted extensions to the following file, including the semver version range:
⚠️ The original.vscode/extensions.jsondoes not support version numbers!
Therefor you might want to migrate (copy/paste) your"unwantedRecommendations"to the new file
Create a file .vscode/extensionsVersionCheck.json, or if you need comments in there, use .jsonc.
⚠️ Therecommendationsfield is not supported. You can easily turn around the logic and define theunwantedRecommendationsto reach the same "goal".
{
// "recommendations": [], !!! NOTE: versions are NOT supported in recommendations !!!
"unwantedRecommendations": [
// Mention the extension id and the version you want to use, it's enough to have 1 single definition.
// However you can also mention the same extension id multiple times with different versions if you preffer.
// We will report only the last matching rule which matches with the installed extension's version.
//
// Exact version: You can specify an exact version like 1.0.0.
"[email protected]",
// Greater than or equal to: You can specify a version greater than or equal to a certain version using >=, like >=1.0.0.
"formulahendry.auto-complete-tag@>=0.1.1",
// Less than: You can specify a version less than a certain version using <, like <2.0.0.
"formulahendry.auto-complete-tag@<0.2.0",
// Hyphen Ranges: You can specify a range of versions using -, like 1.0.0 - 2.0.0. This would include versions greater than or equal to 1.0.0 and less than or equal to 2.0.0.
"[email protected] - 0.9",
// Wildcard Ranges: You can specify a range of versions using *, like 1.0.* or 1.*. This would include all versions that start with 1.0. or 1. respectively.
"formulahendry.auto-complete-tag@0.*",
// Tilde Ranges: You can specify a range of versions using ~, like ~1.0.0. This would include all versions >=1.0.0 and <1.1.0.
"formulahendry.auto-complete-tag@~0.1.0",
// Caret Ranges: You can specify a range of versions using ^, like ^1.0.0. This would include versions >=1.0.0 and <2.0.0.
"formulahendry.auto-complete-tag@^0.1.0"
]
}- It supports SemVer ranges
- The above are all just examples, you should only need to define 1 rule
- However you can feel free to add multiple rules per extension if you need to
- There will be a maximum of 1 notification per extension
- If you save it as
.json, make sure to remove all the comments
You can check the logs if you need more details, what is happening during the checks: VSCode -> OUTPUT -> Unwanted extensions
This extensions runs automatically when you open your project including the one of the configuration files.
You can also execute the check manually, using the vscode command
Check for unwanted extensions
.vscode/extensions.json should contain the list of unwanted extensions within the unwantedRecommendations property.
This file does not support version numbers. See above for details.
Version numbers are only supported within the .vscode/extensionsVersionCheck.json (or .jsonc) file.
You can use the above approach if you are running a workspace.
Just place the .vscode/extensions.json file into your workspace root directory.
Alternatively you can also put the unwanted extensions within your ***.code-workspace file.
{
"extensions": {
"unwantedRecommendations": [
"octref.vetur",
]
}
}What does this extension exactly do?
- When opening the folder/workspace, this extension will automatically run if the
.vscode/extensions.json(or.vscode/extensionsVersionCheck.json) file exists. - If there are any
unwantedRecommendations, it will go through them and check if theextensionis enabled. - It will consider the defined version number as SEMVER, if no version number is defined, it will just look for the extension
- If the extension is enabled, (and the version number matches) it will show a warning message including an info to disabled the extension manually.
- After all extensions are checked, a popup will ask to show all extensions in the extension-gallery.
After the user disabled manually all unwanted extensions, the workspace should be configured as wanted, even after restarts/reboots the extensions will not get enabled automatically. (until you manually enable them again)
-
When opening a project, this extension checks all configured
unwantedRecommendationsand reports the still enabled extensions: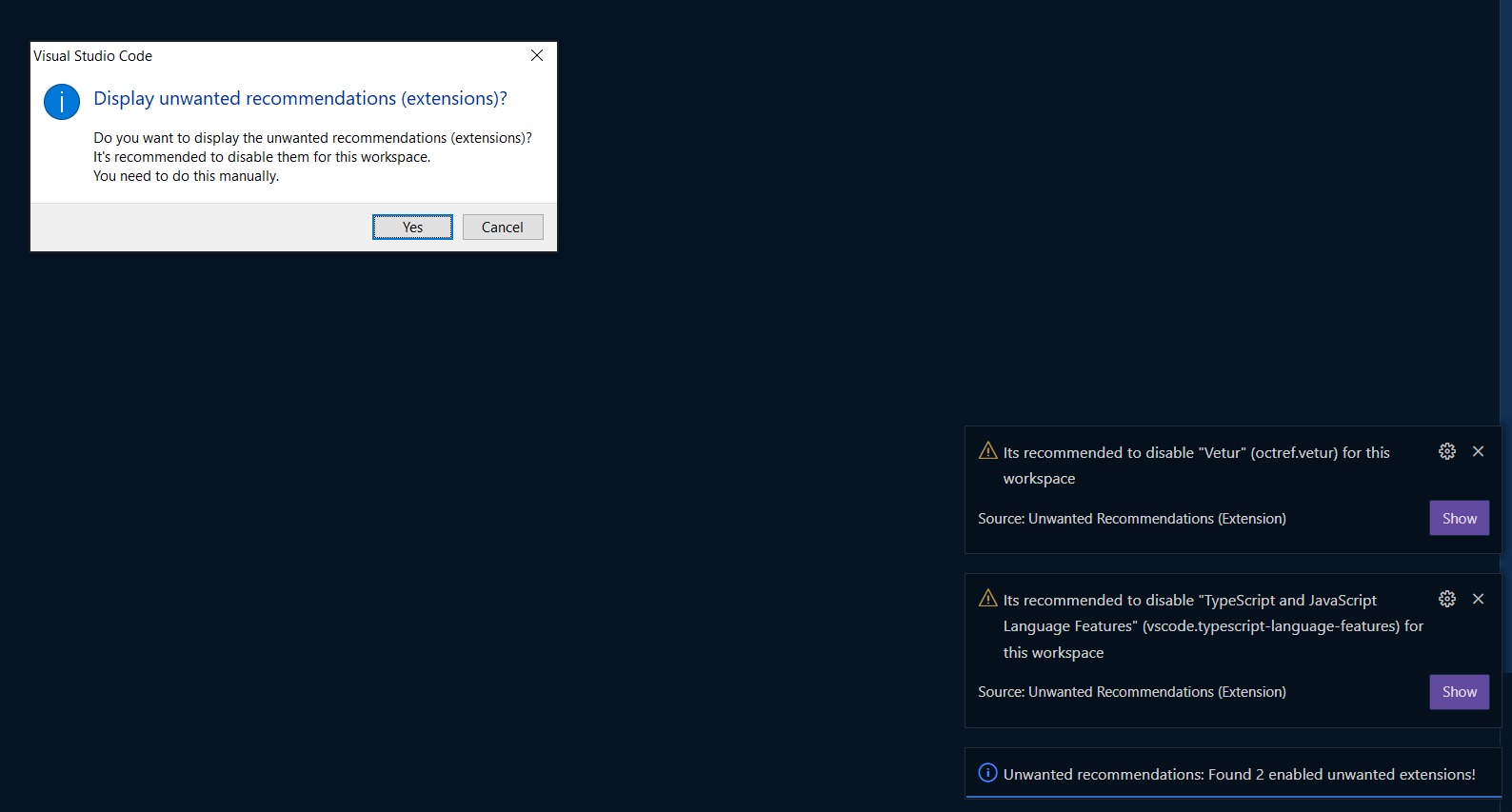
-
After click "yes" on the provided popup, it will bring you to the extensions, to disable them manually: (list will be already filtered to the specific extensions)
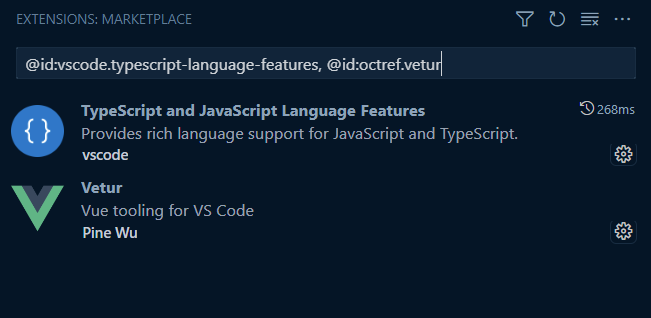
-
You / the user can now disable the extensions manually - preferably using the Disable (Workspace) action
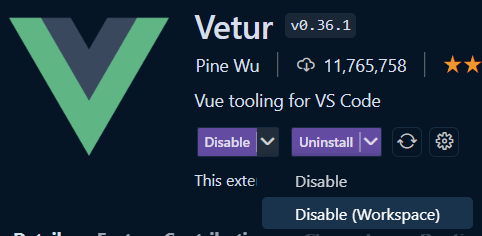
-
On the next restart/reload of vscode, the extension will check again and notify that all is fine (if all
unwantedRecommendations-extensions are disabled)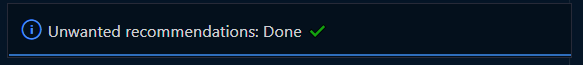
Further when there is no extension defined as unwantedRecommendations, this extension will show the following information:
Current maintenance and improvements are sponsored by Soulcode.
The extension is developed by Fabian Gander aka Cyclodex.
The initial version was sponsored by GARAIO AG.
Thanks a lot!