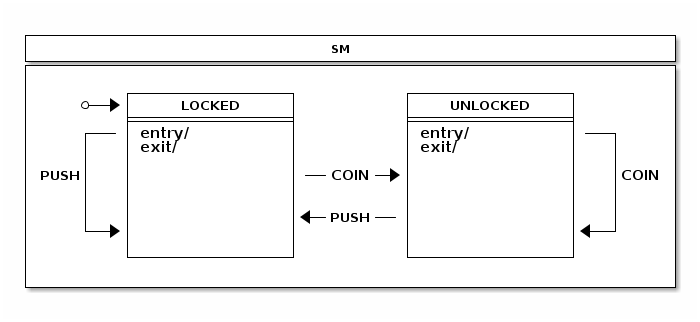
Turnstile是一个简单的设备,如果付款完成,您可以访问该设备,并且使用状态机进行建模非常简单。 最简单的形式是只有两个状态,LOCKED和UNLOCKED。 如果您尝试通过它或您付款,可能会发生两个事件,COIN和PUSH。
状态
public enum States {
LOCKED, UNLOCKED
}
事件
public enum Events {
COIN, PUSH
}
状态机配置
@Configuration
@EnableStateMachine
static class StateMachineConfig
extends EnumStateMachineConfigurerAdapter<States, Events> {
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineStateConfigurer<States, Events> states)
throws Exception {
states
.withStates()
.initial(States.LOCKED) //配置初始状态
.states(EnumSet.allOf(States.class)); //导入所有状态
}
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineTransitionConfigurer<States, Events> transitions)
throws Exception {
transitions //配置transition
.withExternal()
.source(States.LOCKED) //当接收到COIN事件
.target(States.UNLOCKED) //LOCKED--> UNLOCKED
.event(Events.COIN)
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.UNLOCKED) //当接收到PUSH事件
.target(States.LOCKED) //UNLOCKED--> LOCKED
.event(Events.PUSH);
}
}
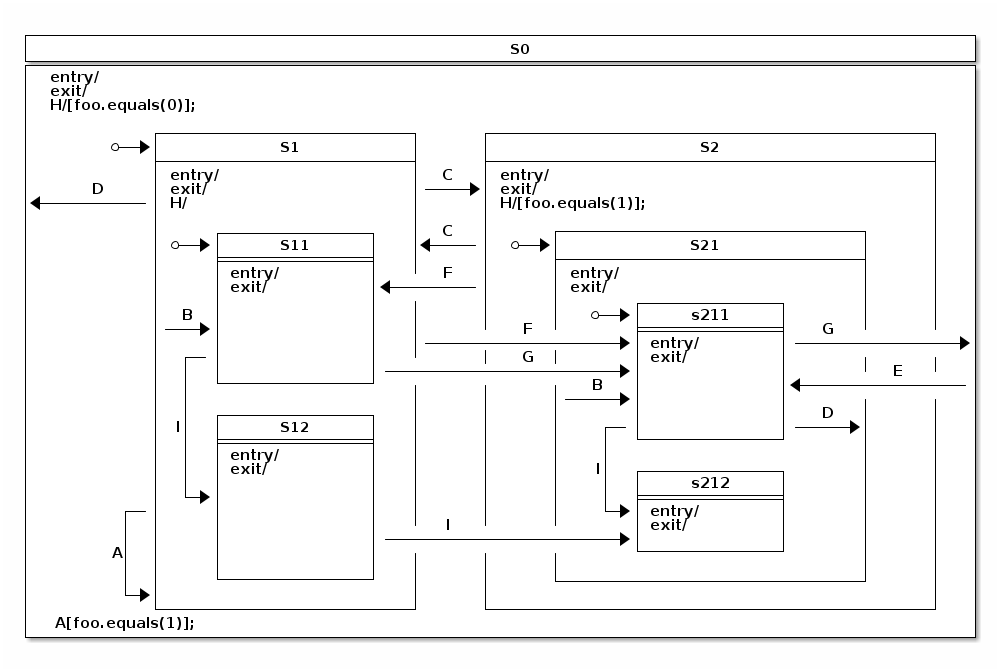
Showcase是一个复杂的状态机,显示所有可能的转换拓扑结构,最多可达四级状态嵌套。
状态
public enum States {
S0, S1, S11, S12, S2, S21, S211, S212
}
事件
public enum Events {
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I
}
状态机配置
状态关系
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineStateConfigurer<States, Events> states)
throws Exception {
states
.withStates()
.initial(States.S0, fooAction()) //初始化状态,初始化动作
.state(States.S0) //导入状态
.and()
.withStates() //配置S0的子状态S1
.parent(States.S0)
.initial(States.S1)
.state(States.S1)
.and()
.withStates() //配置S1的子状态S11、S12
.parent(States.S1)
.initial(States.S11)
.state(States.S11)
.state(States.S12)
.and()
.withStates() //配置S0的子状态S2
.parent(States.S0)
.state(States.S2)
.and()
.withStates() //配置S2的子状态S21、S22
.parent(States.S2)
.initial(States.S21)
.state(States.S21)
.and()
.withStates() //配置S21的子状态S211、S212
.parent(States.S21)
.initial(States.S211)
.state(States.S211)
.state(States.S212);
}
状态转移关系
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineTransitionConfigurer<States, Events> transitions)
throws Exception {
transitions
.withExternal()
.source(States.S1).target(States.S1).event(Events.A) //A:S1->S1
.guard(foo1Guard()) //配置guard
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S1).target(States.S11).event(Events.B) //B:S1->S11
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S21).target(States.S211).event(Events.B) //B:S21->S211
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S1).target(States.S2).event(Events.C) //C:S1->S2
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S2).target(States.S1).event(Events.C) //C:S2->S1
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S1).target(States.S0).event(Events.D) //D:S1->S0
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S211).target(States.S21).event(Events.D) //D:S211->S21
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S0).target(States.S211).event(Events.E) //E:S0->S211
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S1).target(States.S211).event(Events.F) //F:S1->S211
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S2).target(States.S11).event(Events.F) //F:S2->S11
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S11).target(States.S211).event(Events.G) //G:S11->S211
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(States.S211).target(States.S0).event(Events.G) //G:S211->S0
.and()
.withInternal() //内部转移,无状态变化
.source(States.S0).event(Events.H)
.guard(foo0Guard())
.action(fooAction())
.and()
.withInternal() //内部转移,无状态变化
.source(States.S2).event(Events.H)
.guard(foo1Guard())
.action(fooAction())
.and()
.withInternal() //内部转移,无状态变化
.source(States.S1).event(Events.H)
.and()
.withExternal() //I:S11->S12
.source(States.S11).target(States.S12).event(Events.I)
.and()
.withExternal() //I:S211->S212
.source(States.S211).target(States.S212).event(Events.I)
.and()
.withExternal() //I:S12->S212
.source(States.S12).target(States.S212).event(Events.I);
}
action&guard
@Bean
public FooGuard foo0Guard() {
return new FooGuard(0);
}
@Bean
public FooGuard foo1Guard() {
return new FooGuard(1);
}
@Bean
public FooAction fooAction() {
return new FooAction();
}
private static class FooAction implements Action<States, Events> {
@Override
public void execute(StateContext<States, Events> context) {
Map<Object, Object> variables = context.getExtendedState().getVariables();
Integer foo = context.getExtendedState().get("foo", Integer.class);
if (foo == null) {
log.info("Init foo to 0");
variables.put("foo", 0);
} else if (foo == 0) {
log.info("Switch foo to 1");
variables.put("foo", 1);
} else if (foo == 1) {
log.info("Switch foo to 0");
variables.put("foo", 0);
}
}
}
private static class FooGuard implements Guard<States, Events> {
private final int match;
public FooGuard(int match) {
this.match = match;
}
@Override
public boolean evaluate(StateContext<States, Events> context) {
Object foo = context.getExtendedState().getVariables().get("foo");
return !(foo == null || !foo.equals(match));
}
}