| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
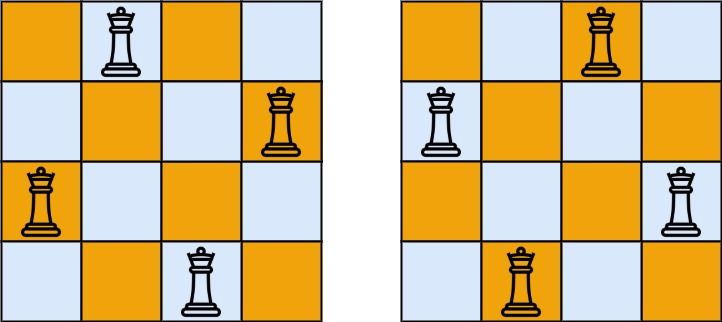
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return the number of distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4 Output: 2 Explanation: There are two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 9
We design a function
In the $i$th row, we enumerate each column of the $i$th row. If the current column does not conflict with the queens placed before, then we can place a queen, and then continue to search the next row, that is, call
If a conflict occurs, then we skip the current column and continue to enumerate the next column.
To determine whether a conflict occurs, we need to use three arrays to record whether a queen has been placed in each column, each positive diagonal, and each negative diagonal, respectively.
Specifically, we use the
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def totalNQueens(self, n: int) -> int:
def dfs(i: int):
if i == n:
nonlocal ans
ans += 1
return
for j in range(n):
a, b = i + j, i - j + n
if cols[j] or dg[a] or udg[b]:
continue
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = True
dfs(i + 1)
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = False
cols = [False] * 10
dg = [False] * 20
udg = [False] * 20
ans = 0
dfs(0)
return ansclass Solution {
private int n;
private int ans;
private boolean[] cols = new boolean[10];
private boolean[] dg = new boolean[20];
private boolean[] udg = new boolean[20];
public int totalNQueens(int n) {
this.n = n;
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
if (i == n) {
++ans;
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int a = i + j, b = i - j + n;
if (cols[j] || dg[a] || udg[b]) {
continue;
}
cols[j] = true;
dg[a] = true;
udg[b] = true;
dfs(i + 1);
cols[j] = false;
dg[a] = false;
udg[b] = false;
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int totalNQueens(int n) {
bitset<10> cols;
bitset<20> dg;
bitset<20> udg;
int ans = 0;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i == n) {
++ans;
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int a = i + j, b = i - j + n;
if (cols[j] || dg[a] || udg[b]) continue;
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = 1;
dfs(i + 1);
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = 0;
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};func totalNQueens(n int) (ans int) {
cols := [10]bool{}
dg := [20]bool{}
udg := [20]bool{}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(i int) {
if i == n {
ans++
return
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
a, b := i+j, i-j+n
if cols[j] || dg[a] || udg[b] {
continue
}
cols[j], dg[a], udg[b] = true, true, true
dfs(i + 1)
cols[j], dg[a], udg[b] = false, false, false
}
}
dfs(0)
return
}function totalNQueens(n: number): number {
const cols: boolean[] = Array(10).fill(false);
const dg: boolean[] = Array(20).fill(false);
const udg: boolean[] = Array(20).fill(false);
let ans = 0;
const dfs = (i: number) => {
if (i === n) {
++ans;
return;
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
let [a, b] = [i + j, i - j + n];
if (cols[j] || dg[a] || udg[b]) {
continue;
}
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = true;
dfs(i + 1);
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = false;
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}function totalNQueens(n) {
const cols = Array(10).fill(false);
const dg = Array(20).fill(false);
const udg = Array(20).fill(false);
let ans = 0;
const dfs = i => {
if (i === n) {
++ans;
return;
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
let [a, b] = [i + j, i - j + n];
if (cols[j] || dg[a] || udg[b]) {
continue;
}
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = true;
dfs(i + 1);
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = false;
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}public class Solution {
public int TotalNQueens(int n) {
bool[] cols = new bool[10];
bool[] dg = new bool[20];
bool[] udg = new bool[20];
int ans = 0;
void dfs(int i) {
if (i == n) {
ans++;
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int a = i + j, b = i - j + n;
if (cols[j] || dg[a] || udg[b]) {
continue;
}
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = true;
dfs(i + 1);
cols[j] = dg[a] = udg[b] = false;
}
}
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
}