| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
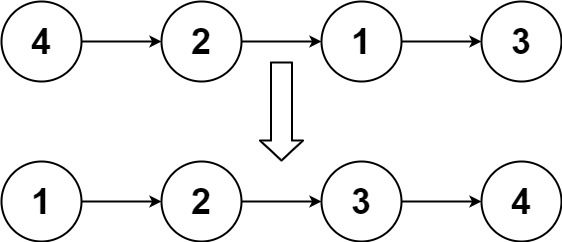
Example 1:
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]
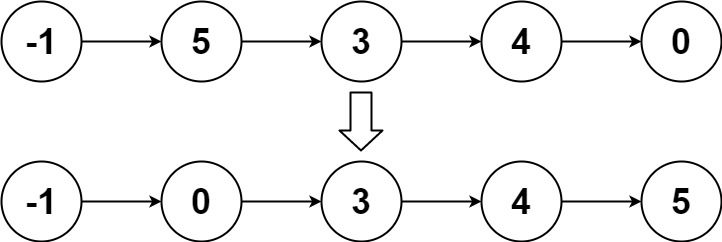
Example 2:
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
We can use the merge sort approach to solve this problem.
First, we use the fast and slow pointers to find the middle of the linked list and break the list from the middle to form two separate sublists
Then, we recursively sort
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
slow, fast = head, head.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
l1, l2 = head, slow.next
slow.next = None
l1, l2 = self.sortList(l1), self.sortList(l2)
dummy = ListNode()
tail = dummy
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
tail = tail.next
tail.next = l1 or l2
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode l1 = head, l2 = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
l1 = sortList(l1);
l2 = sortList(l2);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
tail.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
tail.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return head;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head->next;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode* l1 = head;
ListNode* l2 = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
l1 = sortList(l1);
l2 = sortList(l2);
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode* tail = dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val <= l2->val) {
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func sortList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
slow, fast := head, head.Next
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow, fast = slow.Next, fast.Next.Next
}
l1 := head
l2 := slow.Next
slow.Next = nil
l1 = sortList(l1)
l2 = sortList(l2)
dummy := &ListNode{}
tail := dummy
for l1 != nil && l2 != nil {
if l1.Val <= l2.Val {
tail.Next = l1
l1 = l1.Next
} else {
tail.Next = l2
l2 = l2.Next
}
tail = tail.Next
}
if l1 != nil {
tail.Next = l1
} else {
tail.Next = l2
}
return dummy.Next
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function sortList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
if (head === null || head.next === null) {
return head;
}
let [slow, fast] = [head, head.next];
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next!;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
let [l1, l2] = [head, slow.next];
slow.next = null;
l1 = sortList(l1);
l2 = sortList(l2);
const dummy = new ListNode();
let tail = dummy;
while (l1 !== null && l2 !== null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
tail.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
tail.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = l1 ?? l2;
return dummy.next;
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn sort_list(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
fn merge(l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>, l2: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
match (l1, l2) {
(None, Some(node)) | (Some(node), None) => Some(node),
(Some(mut node1), Some(mut node2)) => {
if node1.val < node2.val {
node1.next = merge(node1.next.take(), Some(node2));
Some(node1)
} else {
node2.next = merge(Some(node1), node2.next.take());
Some(node2)
}
}
_ => None,
}
}
fn sort(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
if head.is_none() || head.as_ref().unwrap().next.is_none() {
return head;
}
let mut head = head;
let mut length = 0;
let mut cur = &head;
while cur.is_some() {
length += 1;
cur = &cur.as_ref().unwrap().next;
}
let mut cur = &mut head;
for _ in 0..length / 2 - 1 {
cur = &mut cur.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
let right = cur.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
merge(sort(head), sort(right))
}
sort(head)
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function (head) {
if (head === null || head.next === null) {
return head;
}
let [slow, fast] = [head, head.next];
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
let [l1, l2] = [head, slow.next];
slow.next = null;
l1 = sortList(l1);
l2 = sortList(l2);
const dummy = new ListNode();
let tail = dummy;
while (l1 !== null && l2 !== null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
tail.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
tail.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = l1 ?? l2;
return dummy.next;
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode SortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode l1 = head, l2 = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
l1 = SortList(l1);
l2 = SortList(l2);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
tail.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
tail.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
}