| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
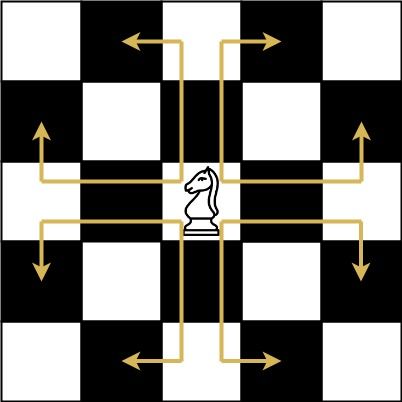
象棋骑士有一个独特的移动方式,它可以垂直移动两个方格,水平移动一个方格,或者水平移动两个方格,垂直移动一个方格(两者都形成一个 L 的形状)。
象棋骑士可能的移动方式如下图所示:
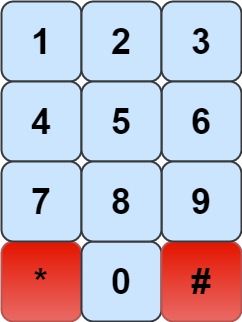
我们有一个象棋骑士和一个电话垫,如下所示,骑士只能站在一个数字单元格上(即蓝色单元格)。
给定一个整数 n,返回我们可以拨多少个长度为 n 的不同电话号码。
你可以将骑士放置在任何数字单元格上,然后你应该执行 n - 1 次移动来获得长度为 n 的号码。所有的跳跃应该是有效的骑士跳跃。
因为答案可能很大,所以输出答案模 109 + 7.
示例 1:
输入:n = 1 输出:10 解释:我们需要拨一个长度为1的数字,所以把骑士放在10个单元格中的任何一个数字单元格上都能满足条件。
示例 2:
输入:n = 2 输出:20 解释:我们可以拨打的所有有效号码为[04, 06, 16, 18, 27, 29, 34, 38, 40, 43, 49, 60, 61, 67, 72, 76, 81, 83, 92, 94]
示例 3:
输入:n = 3131 输出:136006598 解释:注意取模
提示:
1 <= n <= 5000
根据题目描述,我们需要计算出长度为
| 当前数字 | 上一个数字 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 4, 6 |
| 1 | 6, 8 |
| 2 | 7, 9 |
| 3 | 4, 8 |
| 4 | 0, 3, 9 |
| 5 | |
| 6 | 0, 1, 7 |
| 7 | 2, 6 |
| 8 | 1, 3 |
| 9 | 2, 4 |
我们可以通过递推的方式,计算出长度为
然后,我们将
最后,我们将
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def knightDialer(self, n: int) -> int:
f = [1] * 10
for _ in range(n - 1):
g = [0] * 10
g[0] = f[4] + f[6]
g[1] = f[6] + f[8]
g[2] = f[7] + f[9]
g[3] = f[4] + f[8]
g[4] = f[0] + f[3] + f[9]
g[6] = f[0] + f[1] + f[7]
g[7] = f[2] + f[6]
g[8] = f[1] + f[3]
g[9] = f[2] + f[4]
f = g
return sum(f) % (10**9 + 7)class Solution {
public int knightDialer(int n) {
final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
long[] f = new long[10];
Arrays.fill(f, 1);
while (--n > 0) {
long[] g = new long[10];
g[0] = (f[4] + f[6]) % mod;
g[1] = (f[6] + f[8]) % mod;
g[2] = (f[7] + f[9]) % mod;
g[3] = (f[4] + f[8]) % mod;
g[4] = (f[0] + f[3] + f[9]) % mod;
g[6] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[7]) % mod;
g[7] = (f[2] + f[6]) % mod;
g[8] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod;
g[9] = (f[2] + f[4]) % mod;
f = g;
}
return (int) (Arrays.stream(f).sum() % mod);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int knightDialer(int n) {
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
vector<long long> f(10, 1);
while (--n) {
vector<long long> g(10);
g[0] = (f[4] + f[6]) % mod;
g[1] = (f[6] + f[8]) % mod;
g[2] = (f[7] + f[9]) % mod;
g[3] = (f[4] + f[8]) % mod;
g[4] = (f[0] + f[3] + f[9]) % mod;
g[6] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[7]) % mod;
g[7] = (f[2] + f[6]) % mod;
g[8] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod;
g[9] = (f[2] + f[4]) % mod;
f = g;
}
return accumulate(f.begin(), f.end(), 0LL) % mod;
}
};func knightDialer(n int) (ans int) {
f := make([]int, 10)
for i := range f {
f[i] = 1
}
const mod int = 1e9 + 7
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
g := make([]int, 10)
g[0] = (f[4] + f[6]) % mod
g[1] = (f[6] + f[8]) % mod
g[2] = (f[7] + f[9]) % mod
g[3] = (f[4] + f[8]) % mod
g[4] = (f[0] + f[3] + f[9]) % mod
g[6] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[7]) % mod
g[7] = (f[2] + f[6]) % mod
g[8] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod
g[9] = (f[2] + f[4]) % mod
f = g
}
for _, x := range f {
ans = (ans + x) % mod
}
return
}function knightDialer(n: number): number {
const mod = 1e9 + 7;
const f: number[] = Array(10).fill(1);
while (--n) {
const g: number[] = Array(10).fill(0);
g[0] = (f[4] + f[6]) % mod;
g[1] = (f[6] + f[8]) % mod;
g[2] = (f[7] + f[9]) % mod;
g[3] = (f[4] + f[8]) % mod;
g[4] = (f[0] + f[3] + f[9]) % mod;
g[6] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[7]) % mod;
g[7] = (f[2] + f[6]) % mod;
g[8] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod;
g[9] = (f[2] + f[4]) % mod;
f.splice(0, 10, ...g);
}
return f.reduce((a, b) => (a + b) % mod);
}public class Solution {
public int KnightDialer(int n) {
const int mod = 1000000007;
long[] f = new long[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
f[i] = 1;
}
while (--n > 0) {
long[] g = new long[10];
g[0] = (f[4] + f[6]) % mod;
g[1] = (f[6] + f[8]) % mod;
g[2] = (f[7] + f[9]) % mod;
g[3] = (f[4] + f[8]) % mod;
g[4] = (f[0] + f[3] + f[9]) % mod;
g[6] = (f[0] + f[1] + f[7]) % mod;
g[7] = (f[2] + f[6]) % mod;
g[8] = (f[1] + f[3]) % mod;
g[9] = (f[2] + f[4]) % mod;
f = g;
}
return (int)(f.Sum() % mod);
}
}我们假设
由于
依次类推,我们可以得到矩阵
我们定义初始矩阵 $res = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \cdots 1 \end{bmatrix}$,与
时间复杂度
import numpy as np
base = [
(0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0),
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0),
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1),
(0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0),
(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1),
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0),
(1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0),
(0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0),
(0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0),
(0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0),
]
class Solution:
def knightDialer(self, n: int) -> int:
factor = np.asmatrix(base, np.dtype("O"))
res = np.asmatrix([[1] * 10], np.dtype("O"))
n -= 1
mod = 10**9 + 7
while n:
if n & 1:
res = res * factor % mod
factor = factor * factor % mod
n >>= 1
return res.sum() % modclass Solution {
private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
private final int[][] base = {{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
public int knightDialer(int n) {
int[][] res = pow(base, n - 1);
int ans = 0;
for (int x : res[0]) {
ans = (ans + x) % mod;
}
return ans;
}
private int[][] mul(int[][] a, int[][] b) {
int m = a.length, n = b[0].length;
int[][] c = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < b.length; ++k) {
c[i][j] = (int) ((c[i][j] + 1L * a[i][k] * b[k][j] % mod) % mod);
}
}
}
return c;
}
private int[][] pow(int[][] a, int n) {
int[][] res = new int[1][a.length];
Arrays.fill(res[0], 1);
while (n > 0) {
if ((n & 1) == 1) {
res = mul(res, a);
}
a = mul(a, a);
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int knightDialer(int n) {
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
vector<vector<int>> base = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
vector<vector<int>> res = pow(base, n - 1, mod);
return accumulate(res[0].begin(), res[0].end(), 0LL) % mod;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> mul(const vector<vector<int>>& a, const vector<vector<int>>& b, int mod) {
int m = a.size(), n = b[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> c(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < b.size(); ++k) {
c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + (1LL * a[i][k] * b[k][j]) % mod) % mod;
}
}
}
return c;
}
vector<vector<int>> pow(vector<vector<int>>& a, int n, int mod) {
int size = a.size();
vector<vector<int>> res(1, vector<int>(size, 1));
while (n > 0) {
if (n % 2 == 1) {
res = mul(res, a, mod);
}
a = mul(a, a, mod);
n /= 2;
}
return res;
}
};const mod = 1e9 + 7
func knightDialer(n int) int {
base := [][]int{
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
}
res := pow(base, n-1)
ans := 0
for _, x := range res[0] {
ans = (ans + x) % mod
}
return ans
}
func mul(a, b [][]int) [][]int {
m := len(a)
n := len(b[0])
c := make([][]int, m)
for i := range c {
c[i] = make([]int, n)
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
for k := 0; k < len(b); k++ {
c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + a[i][k]*b[k][j]) % mod
}
}
}
return c
}
func pow(a [][]int, n int) [][]int {
size := len(a)
res := make([][]int, 1)
res[0] = make([]int, size)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
res[0][i] = 1
}
for n > 0 {
if n%2 == 1 {
res = mul(res, a)
}
a = mul(a, a)
n /= 2
}
return res
}const mod = 1e9 + 7;
function knightDialer(n: number): number {
const base: number[][] = [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
];
const res = pow(base, n - 1);
let ans = 0;
for (const x of res[0]) {
ans = (ans + x) % mod;
}
return ans;
}
function mul(a: number[][], b: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = a.length;
const n = b[0].length;
const c: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (let k = 0; k < b.length; k++) {
c[i][j] =
(c[i][j] + Number((BigInt(a[i][k]) * BigInt(b[k][j])) % BigInt(mod))) % mod;
}
}
}
return c;
}
function pow(a: number[][], n: number): number[][] {
const size = a.length;
let res: number[][] = Array.from({ length: 1 }, () => Array(size).fill(1));
while (n > 0) {
if (n % 2 === 1) {
res = mul(res, a);
}
a = mul(a, a);
n = Math.floor(n / 2);
}
return res;
}