The Knowledge Graph project uses large language models to extract entities, atomic facts, and relationships from long texts and organizes them into a Neo4j graph database. A graph reader agent uses complex reasoning and multi-hop queries to find insights from interconnected data.
First, you will need to download the graph database server, neo4j, and configure a local database instance. Tutorials can be found on their website.
Second, you will need an OpenAI API key to run model inference. The system also currently uses HuggingFace serverless inference, which requires a HuggingFace API key.
From the project directory, create and activate a virtual environment:
python3.12 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Install project dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Create a .env file in the project root and add the following values:
HF_API_KEY=your-key-here
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-key-here
NEO4J_URI=your-uri
NEO4J_USERNAME=your-username
NEO4J_PASSWORD=your-password
NEO4J_DATABASE=your-database
From the root of the project directory, the program will run with the following command:
python src/main.py {command} {args}
Reset:
If this is your first time using a new database instance, or if you would like to reset your database, run the following command. This will erase all data in the database and create useful graph constraints.
python src/main.py reset
Build:
Use the following command to build a graph based on a Wikipedia article of the provided subject. You can run this many times with various subjects to build a large, interconnected knowledge graph.
python src/main.py build "Harry Potter"
Read:
Use the following command to answer questions based on the data in your knowledge graph. The system uses agent reasoning and RAG to extract entities, facts, and text snippets, eventually forming a rational answer.
python src/main.py read "What school did the author of the Harry Potter books attend?"
Expand:
Coming Soon. Eventually, I plan to add an expand function which will use various factors and LLM reasoning to determine the most important nodes for further research.
For example, if the original graph is trained on the Harry Potter Wikipedia article, the system may determine that certain nodes require more research, such as J.K. Rowling, Daniel Radcliffe, and Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone (film).
python src/main.py expand 3
The Graph Builder component processes long-form text such as Wikipedia articles, and extracts key entities, relationships, and atomic facts to construct a knowledge graph. This graph is stored in a Neo4j database for efficient querying and visualization.
- Large Language Model: Utilizes
meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instructto generate XML-based responses for structured extraction of entities and relationships. - Embeddings: Key entities are embedded using
sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2, enabling similarity-based retrieval for the graph reader agent. - Python Libraries: Built with LangChain to facilitate AI interactions and manage chat history.
- Database: Neo4j stores all extracted nodes, edges, and relationships.
- Prompt Logging: Prompts and LLM outputs are versioned and timestamped for debugging and iterative improvement.
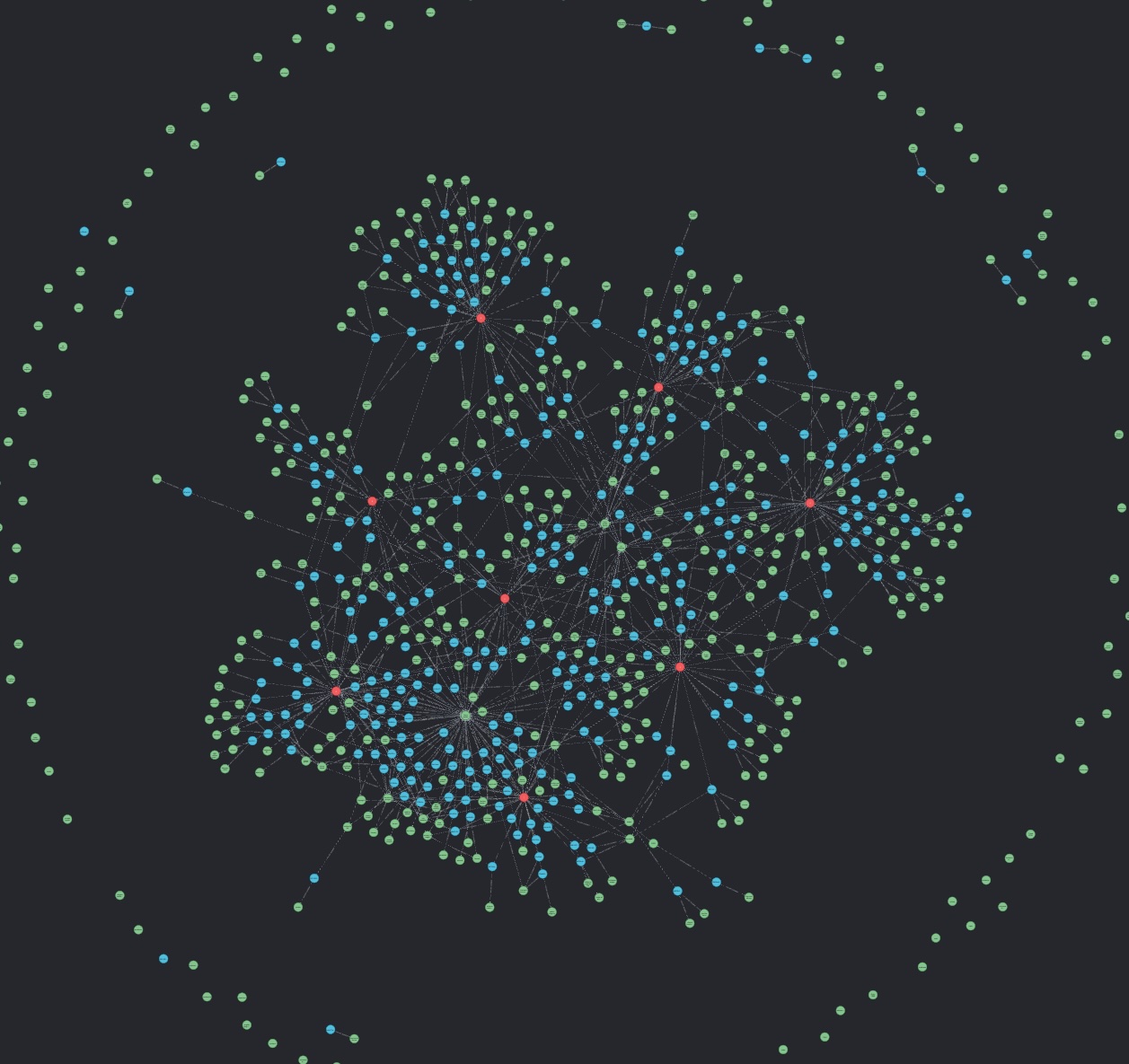
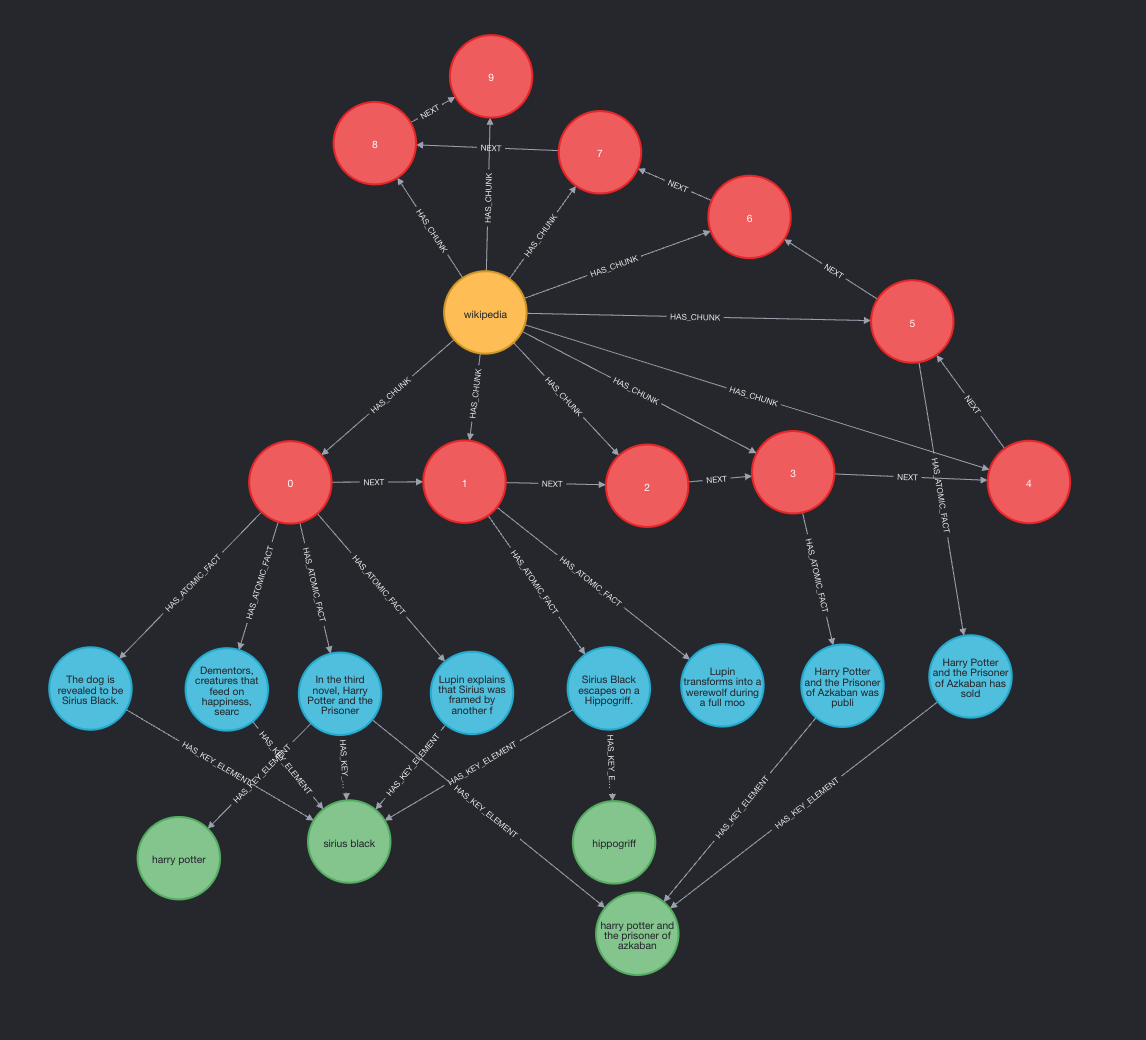
The Graph Reader is a querying agent designed to form a rational plan, traverse the knowledge graph, and form answers to complex, multi-hop questions. By leveraging embeddings and graph-based reasoning, it creates responses that traditional RAG approaches struggle with.
- Large Language Model: Utilizes
openai/GPT-4owith structured output and tool calling to power the graph reader agent. - Python Libraries: Built with LangChain and LangGraph to manage agent state and action selection.
- Vector Search and Graph Traversal: Matches embeddings to find relevant entities and context. If the answer is not found, neighbor nodes are explored in Neo4j to form multi-hop responses.
----- Initial -----
Question: A popular novel was compared by the Sunday Times to works by Roald Dahls. How many copies of this novel have been sold?
----- Step: 1 -----
Rational Plan: To answer the question about how many copies of the novel have been sold, we need to:
1. Identify the novel that was compared by the Sunday Times to works by Roald Dahl.
2. Find specific sales figures or estimates for this novel, which might be mentioned in the article.
3. Provide the number of copies sold based on the information available in the article.
----- Step: 2 -----
Check Atomic Facts Queue: ['the sunday times', 'roald dahl', 'book sales', '8.3 million copies', '10.8 million copies']
>>> returned atomic facts shown in graph screenshot.
----- Step: 3 -----
Read Chunk: ['d112ff4558f29fcb3077101f5ada5229']
>>> returned a chunk of text (identified by hash) from the original article related to the above facts.
----- Step: 4 -----
Next Action: Termination
Rational for Next Action: The current chunk provides the sales figures for Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone, which is the novel compared to Roald Dahl's works by the Sunday Times. Therefore, the information needed to answer the question is complete.
----- Step: 5 -----
Analysis: The notebook entry provides a direct answer to the question. It states that the novel Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone was compared by the Sunday Times to works by Roald Dahl and that it has sold 120 million copies. There is no conflicting information or need for further analysis as the notebook content is clear and directly answers the question.
Answer: The novel has sold 120 million copies.
----- Return -----
Answer: The novel has sold 120 million copies.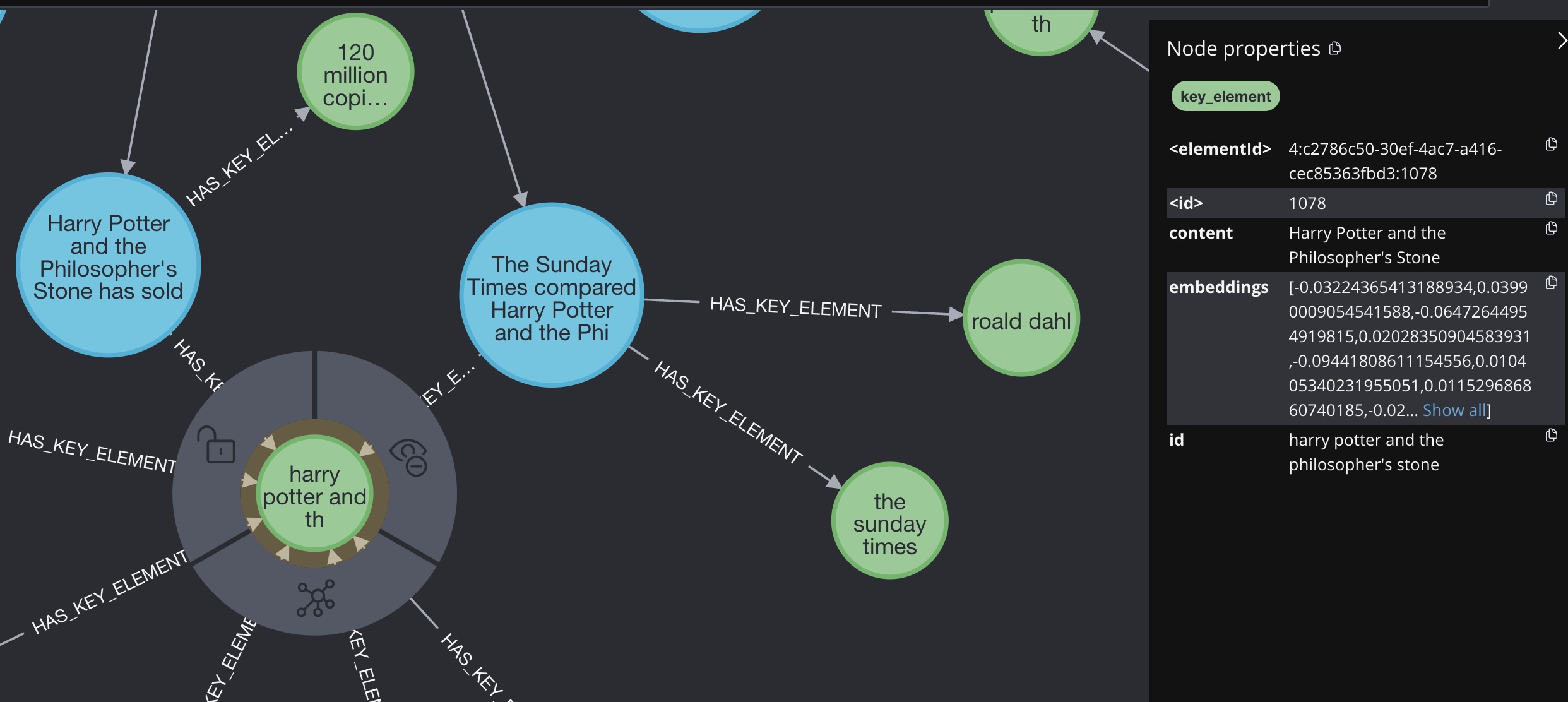
This code is heavily inspired by the following research:
GraphReader: Building Graph-based Agent to Enhance Long-Context Abilities of Large Language Models by Li et al.
Implementing GraphReader with Neo4j and LangGraph by Tomaz Bratanic