Given a multidimensional array with depth of n, flatten it. Once flattened make it available as a method on array instance
[
[1, 2, 3],
3,
'',
true,
[[1,[2,3,[4]]]]
]
[1, 2, 3, 3, "", true, 1, 2, 3, 4]
const flattenArray = (array) => {
return array.reduce(function (acc, element) {
if (element instanceof Array) {
acc = acc.concat(flatMap(element));
} else {
acc.push(element);
}
return acc;
}, []);
};
const data = [[1, 2, 3], 3, "", true, [[1, [2, 3, [4]]]]];
const expected = [1, 2, 3, 3, "", true, 1, 2, 3, 4];
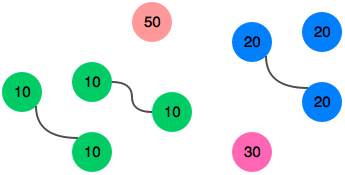
console.assert(flattenArray(data).length === expected.length, "Oh no!");Given an array of integers, determine how many pairs of matching integers there are. For example, in an array of length 7, sampleArray = [1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 3, 2], there is one pair of 1's and one pair of 2's. There are three unpaired numbers left, a 1, a 2 and a 3. The number of pairs is 2.
Complete the numberPairs function in the editor below. It must return the number of matching pairs in the array. numberPairs has the following parameter(s):
- n: the length of the array
- a: the array of numbers
The first line contains an integer n, the length of the array. The second line contains n space-separated integers within the array.
- 1 <= n <= 100
- The numbers contained in the array a are between 1 and 100
Return the total number of matching pairs of numbers
9
10 20 20 10 10 30 50 10 20
3
function numberPairs(n, ar) {
const indices = new Set()
return ar.reduce(function (result, currentNumber, index, ar) {
if (!indices.has(index)) {
for(let i = index + 1; i < n; i++) {
if (ar[i] === currentNumber) {
indices.add(i)
result++
break
}
}
}
return result
}, 0)
}Emma is playing a new mobile game that starts with consecutively numbered clouds. Some of the clouds are dangerous rain clouds, but others are safe, normal clouds. She can jump on any cloud having a number that is equal to the number of the current cloud plus 1 or 2 (meaning she can only skip over a maximum of one cloud). She must avoid the rain clouds. Determine the minimum number of jumps it will take Emma to jump from her starting position to the last cloud. It is always possible to win the game.
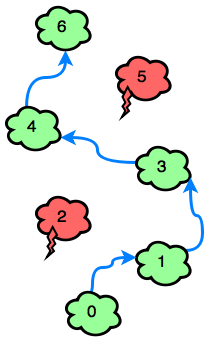
For each game, Emma will get an array of clouds, each with a number 0 or 1: 0 if they are safe or 1 if they must be avoided. For example, c = [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]. The number on each cloud is its index in the list so she must avoid the clouds at indexes 1 and 5. She could follow the following two paths: 0→2→4→6 or 0→2→3→4→6. The first path takes 3 jumps while the second takes 4.
Complete the jumpingOnClouds function in the editor below. It should return the minimum number of jumps required, as an integer.
jumpingOnClouds has the following parameter:
- c: an array of 0s and 1s
The first line contains an integer n, the total number of clouds. The second line contains n space-separated 0s and 1s describing clouds.
- n <= 100
- The first and last cloud must be labeled 0
Print the minimum number of jumps needed to win the game.
7
0 0 1 0 0 1 0
4
Emma must avoid c[2] and c[5]. She can win the game with a minimum of 4 jumps:
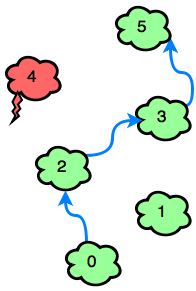
6
0 0 0 0 1 0
3
The only cloud to avoid is c[4]. Emma can win the game in 3 jumps:
function jumpingOnClouds(c) {
let jumps = 0
for (let i = 1; i < c.length; i++) {
if (c[i] === 0) {
if (c[i+1] === 0 && c[i-1] !== 1) i++
jumps++
}
}
return jumps
}A left rotation operation on an array shifts each of the array's elements 1 unit to the left. For example, if 2 left rotations are performed on array [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], then the array would become [3, 4, 5, 1, 2].
Given an array a of n integers and a number, d, perform d left rotations on the array. Return the updated array to be printed as a single line of space-separated integers.
Complete the function rotLeft in the editor below. It should return the resulting array of integers. rotLeft has the following parameter(s):
- An array of integers a.
- An integer d, the number of rotations.
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and d, the size of a and the number of left rotations you must perform. The second line contains n space-separated integers a[i].
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
- 1 <= d <= n
- 1 <= a[i] <= 10^6
Print a single line of n space-separated integers denoting the final state of the array after performing d left rotations.
5 4
1 2 3 4 5
5 1 2 3 4
When we perform d = 4 left rotations, the array undergoes the following sequence of changes: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] -> [2, 3, 4, 5, 1] -> [3, 4, 5, 1, 2] -> [4, 5, 1, 2, 3] -> [5, 1, 2, 3, 4]
- Brute force
function rotLeft(a, d) {
const result = [...a]
for (let i = 0; i < d; i++) {
const first = result.shift()
result.push(first)
}
return result
}- Optimal solution
function rotLeft(a, d) {
const result = [...a]
for (let i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
result[i] = a[(i + d) % a.length]
}
return result
}Given a 6 x 6 2D Array, arr:
1 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
An hourglass in A is a subset of values with indices falling in this pattern in arr's graphical representation:
a b c
d
e f g
There are 16 hourglasses in arr. An hourglass sum is the sum of an hourglass' values. Calculate the hourglass sum for every hourglass in arr, then print the maximum hourglass sum. The array will always be 6 x 6.
arr =
-9 -9 -9 1 1 1
0 -9 0 4 3 2
-9 -9 -9 1 2 3
0 0 8 6 6 0
0 0 0 -2 0 0
0 0 1 2 4 0
The 16 hourglass sums are:
-63, -34, -9, 12,
-10, 0, 28, 23,
-27, -11, -2, 10,
9, 17, 25, 18
The highest hourglass sum is 28 from the hourglass beginning at row 1, column 2:
0 4 3
1
8 6 6
Note: If you have already solved the Java domain's Java 2D Array challenge, you may wish to skip this challenge.
Complete the function hourglassSum in the editor below. hourglassSum has the following parameter(s):
- int arr[6][6]: an array of integers
- int: the maximum hourglass sum
Each of the 6 lines of inputs arr[i] contains 6 space-separated integers arr[i][j].
- -9 <= arr[i][j] <= 9
- 0 <= i, j <= 5
Print the largest (maximum) hourglass sum found in arr.
1 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 2 4 4 0
0 0 0 2 0 0
0 0 1 2 4 0
19
arr contains the following hourglasses:
The hourglass with the maximum sum (19) is:
2 4 4
2
1 2 4
function hourglassSum(arr) {
const values = []
const maxRowCol = arr.length - 2
for (let i = 0; i < maxRowCol; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < maxRowCol; j++) {
values.push(
arr[i][j] + arr[i][j+1] + arr[i][j+2] +
arr[i+1][j+1] +
arr[i+2][j] + arr[i+2][j+1] + arr[i+2][j+2]
)
}
}
return Math.max(...values)
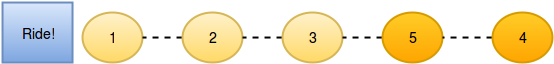
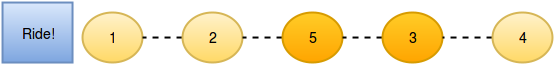
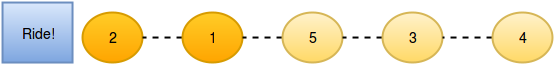
}There are people waiting in line for a rollercoaster ride, and each person wears a sticker indicating their initial position in the queue. Initial positions increment by 1 from 1 at the front of the line to n at the back. Any person in the queue can ask the person directly in front of them to swap positions. If two people swap positions, they still wear the same sticker denoting their original places in line. One person can swap with at most two others. For example, if n = 8 and Person 5 swaps with Person 4, the queue will look like this: 1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, 8. Fascinated by this chaotic queue, you decide you must know the minimum number of swaps that took place to get the queue into its current state!
Complete the function minimumSwaps in the editor below. It must print an integer representing the minimum number of swaps necessary, or Too chaotic if the line configuration is not possible.
minimumSwaps has the following parameter(s):
- q_count: the length of the array
- q: an array of integers
The first line contains an integer t, the number of test cases. Each of the next t pairs of lines are as follows:
- The first line contains an integer t, the number of people in the queue
- The second line has n space-separated integers describing the final state of the queue.
- 1 <= t <= 10
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
Print an integer denoting the minimum number of swaps needed to get the queue into its final state. Print Too chaotic if the state is invalid, i.e. it requires a person to have swapped with more than 2 people.
2
5
2 1 5 3 4
5
2 5 1 3 4
3
Too chaotic
Test Case 1 The initial state:
After person 5 moves one position ahead by asking person 4:
Now person 5 moves another position ahead by asking person 3:
And person 2 moves one position ahead by asking person 1:
So the final state is 2, 1, 5, 3, 4 after three swapping operations.
Test Case 2 No person can swap with more than two people, so it's not possible to achieve the input state.
// Complete the minimumSwaps function below.
function minimumSwaps(q) {
var result = 0
let expectedFirst = 1
let expectedSecond = 2
let expectedThird = 3
for (let i = 0; i < q.length; i++) {
const currentValue = q[i]
if (currentValue === expectedFirst) {
expectedFirst = expectedSecond
expectedSecond = expectedThird
++expectedThird
} else if (currentValue === expectedSecond) {
++result
expectedSecond = expectedThird
++expectedThird
} else if (currentValue === expectedThird) {
result += 2
++expectedThird
} else {
result = "Too chaotic"
break
}
}
console.log(result)
return result
}You are given an unordered array consisting of consecutive integers [1, 2, 3, ..., n] without any duplicates. You are allowed to swap any two elements. You need to find the minimum number of swaps required to sort the array in ascending order.
For example, given the array arr = [7, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6] we perform the following steps:
i arr swap (indices)
0 [7, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6] swap (0,3)
1 [2, 1, 3, 7, 4, 5, 6] swap (0,1)
2 [1, 2, 3, 7, 4, 5, 6] swap (3,4)
3 [1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 5, 6] swap (4,5)
4 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 6] swap (5,6)
5 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
It took 5 swaps to sort the array.
Complete the function minimumSwaps in the editor below. It must return an integer representing the minimum number of swaps to sort the array. minimumSwaps has the following parameter(s):
- arr: an unordered array of integers
The first line contains an integer, n, the size of arr. The second line contains n space-separated integers arr[i].
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
- 1 <= arr[i] <= n
Return the minimum number of swaps to sort the given array.
4
4 3 1 2
3
Given array arr : [4, 3, 1, 2] After swapping (0, 2) we get arr: [1, 3, 4, 2] After swapping (1, 2) we get arr: [1, 4, 3, 2] After swapping (1, 3) we get arr: [1, 2, 3, 4] So, we need a minimum of 3 swaps to sort the array in ascending order.
5
2 3 4 1 5
3
Given array arr : [2, 3, 4, 1, 5] After swapping (2, 3) we get arr: [2, 3, 1, 4, 5] After swapping (0, 1) we get arr: [3, 2, 1, 4, 5] After swapping (0, 2) we get arr: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] So, we need a minimum of 3 swaps to sort the array in ascending order.
7
1 3 5 2 4 6 7
3
Given array arr : [1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6, 7] After swapping (1, 3) we get arr: [1, 2, 5, 3, 4, 6, 7] After swapping (2, 3) we get arr: [1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6, 7] After swapping (3, 4) we get arr: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] So, we need a minimum of 3 swaps to sort the array in ascending order.
// Complete the minimumSwaps function below.
function minimumSwaps(arr) {
let swaps = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){
if(arr[i] !== i+1) {
arr[arr.lastIndexOf(i+1)] = arr[i];
swaps++;
}
}
return swaps;
}You will be given an array of integers and a target value. Determine the number of pairs of array elements that have a difference equal to a target value. For example, given an array of [1, 2, 3, 4] and a target value of 1, we have three values meeting the condition: 2 - 1 = 1,** 3 - 2 = 1** and 4 - 3 = 1.
Complete the pairs function below. It must return an integer representing the number of element pairs having the required difference. pairs has the following parameter(s):
- k: an integer, the target difference
- arr: an array of integers
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and k, the size of arr and the target value. The second line contains n space-separated integers of the array arr.
- 2 <= n <= 10^5
- 0 < k < 10^9
- 0 < arr[i] < 2^31 - 1
- each integer arr[i] will be unique
An integer representing the number of pairs of integers whose difference is k.
5 2
1 5 3 4 2
3
There are 3 pairs of integers in the set with a difference of 2: [5,3], [4,2] and [3,1] .
// Complete the pairs function below.
function pairs(k, arr) {
let pairs = 0
const memo = {}
const sortDesc = arr.sort((a, b) => b-a)
for(let i = 0; i < sortDesc.length; i++) {
if (sortDesc[i] > k) {
if (memo[sortDesc[i]]) {
pairs++
continue
}
const diff = sortDesc[i] - k
for (let j = i + 1; j < sortDesc.length; j++) {
if (sortDesc[j] === diff) {
memo[sortDesc[i]] = 1
pairs++
break
}
}
} else {
break
}
}
return pairs
}The median of a set of integers is the midpoint value of the data set for which an equal number of integers are less than and greater than the value. To find the median, you must first sort your set of integers in non-decreasing order, then:
- If your set contains an odd number of elements, the median is the middle element of the sorted sample. In the sorted set {1, 2, 3}, 2 is the median.
- If your set contains an even number of elements, the median is the average of the two middle elements of the sorted sample. In the sorted set {1, 2, 3, 4}, (2+3)/2 = 2.5 is the median.
Given an input stream of n integers, you must perform the following task for each i^th integer:
- Add the i^th integer to a running list of integers.
- Find the median of the updated list (i.e., for the first element through the i^th element).
- Print the list's updated median on a new line. The printed value must be a double-precision number scaled to 1 decimal place (i.e., 12.3 format).
The first line contains a single integer, n, denoting the number of integers in the data stream. Each line i of the n subsequent lines contains an integer, ai, to be added to your list.
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
- 0 <= ai <= 10^5
After each new integer is added to the list, print the list's updated median on a new line as a single double-precision number scaled to 1 decimal place (i.e., 12.3 format).
6
12
4
5
3
8
712.0
8.0
5.0
4.5
5.0
6.0There are n = 6 integers, so we must print the new median on a new line as each integer is added to the list:
- list = {12}, median = 12.0
- list = {12, 4} -> {4, 12}, median = (12+4)/2 = 8.0
- list = {12, 4, 5} -> {4, 5, 12}, median = 5.0
- list = {12, 4, 5, 3} -> {3, 4, 5, 12}, median = (4+5)/2 = 4.5
- list = {12, 4, 5, 3, 8} -> {3, 4, 5, 8, 12}, median = 5.0
- list = {12, 4, 5, 3, 8, 7} -> {3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 12}, median = (5+7)/2 = 6.0
function insertSorted(arr, num) {
let low = 0
let high = arr.length
while (low < high) {
const mid = Math.floor(low + (high-low)/2)
if (arr[mid] - num > 0) {
high = mid
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
}
arr.splice(low, 0, num)
}
function runningMedian(list) {
/*
* Write your code here.
*/
const addNumber = (arr, num) => arr.push((num).toFixed(1))
const items = []
return list.reduce((result, item, index) => {
if (index === 0) {
items.push(item)
addNumber(result, item)
} else {
insertSorted(items, item)
const mid = items.length / 2
const median = items.length % 2 === 0 ? (
(items[mid - 1] + items[mid])/2
) : (
items[Math.ceil(mid) - 1]
)
addNumber(result, median)
}
return result
}, [])
}Starting with a 1-indexed array of zeros and a list of operations, for each operation add a value to each of the array element between two given indices, inclusive. Once all operations have been performed, return the maximum value in your array. For example, the length of your array of zeros n = 10. Your list of queries is as follows:
a b k
1 5 3
4 8 7
6 9 1
Add the values of k between the indices a and b inclusive:
index → 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
[0,0,0, 0, 0,0,0,0,0, 0]
[3,3,3, 3, 3,0,0,0,0, 0]
[3,3,3,10,10,7,7,7,0, 0]
[3,3,3,10,10,8,8,8,1, 0]
The largest value is 10 after all operations are performed.
Complete the function arrayManipulation in the editor below. It must return an integer, the maximum value in the resulting array.. arrayManipulation has the following parameters:
- n - the number of elements in your array.
- queries - a two dimensional array of queries where each queries[i] contains three integers, a, b and k.
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and m, the size of the array and the number of operations. Each of the next m lines contains three space-separated integers a, b and k, the left index, right index and summand.
- 3 <= n <= 10^7
- 1 <= m <= 2*10^5
- 1 <= a <= b <= n
- 0 <= k <= 10^9
Return the integer maximum value in the finished array.
5 3
1 2 100
2 5 100
3 4 100
200
After the first update list will be 100 100 0 0 0.
After the second update list will be 100 200 100 100 100.
After the third update list will be 100 200 200 200 100.
The required answer will be 200.
- Brute force 1 - O(n*k)
function arrayManipulation(n, queries) {
const operations = new Array(n).fill(0)
let maxValue = 0
for (let i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
const a = queries[i][0]
const b = queries[i][1]
const k = queries[i][2]
for (let j = a - 1; j < b; j++) {
operations[j] += k
if (operations[j] > maxValue) maxValue = operations[j]
}
}
return maxValue
}- Brute force 2 - O(n*k)
function arrayManipulation(n, queries) {
let maxValue = 0
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
let value = 0
for (let j = 0; j < queries.length; j++) {
const a = queries[j][0]
const b = queries[j][1]
const k = queries[j][2]
if (a <= i && i <= b) value += k
}
if (value > maxValue) maxValue = value
}
return maxValue
}- Optimal solution - O(k+n)
function arrayManipulation(n, queries) {
const operations = new Array(n).fill(0)
let maxValue = 0
for (let i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
const a = queries[i][0]
const b = queries[i][1]
const k = queries[i][2]
operations[a-1] += k
operations[b] -= k
}
let sum = 0
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += operations[i]
maxValue = Math.max(sum, maxValue)
}
return maxValue
}Given a two dimensional array (matrix) with dimensions mxn, fill it in a spiral pattern, starting with 1 and continuing until filled.
4
1 2 3 4
12 13 14 5
11 16 15 6
10 9 8 7
5
1 2 3 4 5
16 17 18 19 6
15 24 25 20 7
14 23 22 21 8
13 12 11 10 9
function generateMatrix(n) {
// create an empty two dimensional array
const result = new Array(n).fill().map(() => new Array(n).fill(0));
let count = 1;
let startCol = 0;
let endCol = n - 1;
let startRow = 0;
let endRow = n - 1;
// iterate until we found the last inner spiral
while (startCol <= endCol && startRow <= endRow) {
// fill to right
for (let i = startCol; i <= endCol; i++) {
result[startRow][i] = count;
count++;
}
// increment start row for next time
startRow++;
// fill to down
for (let j = startRow; j <= endRow; j++) {
result[j][endCol] = count;
count++;
}
// decrement end col for next time
endCol--;
// fill to left
for (let i = endCol; i >= startCol; i--) {
result[endRow][i] = count;
count++;
}
// decrement end row for next time
endRow--;
// fill to top
for (let i = endRow; i >= startRow; i--) {
result[i][startCol] = count;
count++;
}
// increment start col for next time
startCol++;
}
return result;
}Given an array of lines of code, remove single and block comments and return the not empty lines.
function removeCommentsFromCodeLines(linesOfCode) {
const result = [];
let foundBlockComment = false;
for (let i = 0; i < linesOfCode.length; i++) {
let string = linesOfCode[i];
string = string.replace(/\/\/.*/, "").replace(/\/\*.*\//, "");
if (foundBlockComment) {
const indexEndBlockComment = string.indexOf("*/");
if (indexEndBlockComment > -1) {
const substring = string.substring(0, indexEndBlockComment + 2);
string = string.replace(substring, "");
foundBlockComment = false;
} else {
string = "";
}
}
const indexStartBlockComment = string.indexOf("/*");
if (!foundBlockComment && indexStartBlockComment > -1) {
// replace substring from beggining of block comment until end line
const substring = string.substring(indexStartBlockComment);
string = string.replace(substring, "");
foundBlockComment = true;
}
const newLine = string.trim();
if (newLine.length) {
result.push(newLine);
}
}
return result;
}test("should remove comments correctly", () => {
const lines = `
// Single line comment
/* Block comment */
/*
* Multiple lines /*
*/ function lol() {} /*
fdfddf dffdfddf df df
*/
// Function to add two numbers
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b; // Return the sum
}
`.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/);
const result = removeCommentsFromCodeLines(lines);
expect(result.length).toBe(
["function lol() {} ", "function sum(a, b) {", "return a + b;", "}"].length
);
});