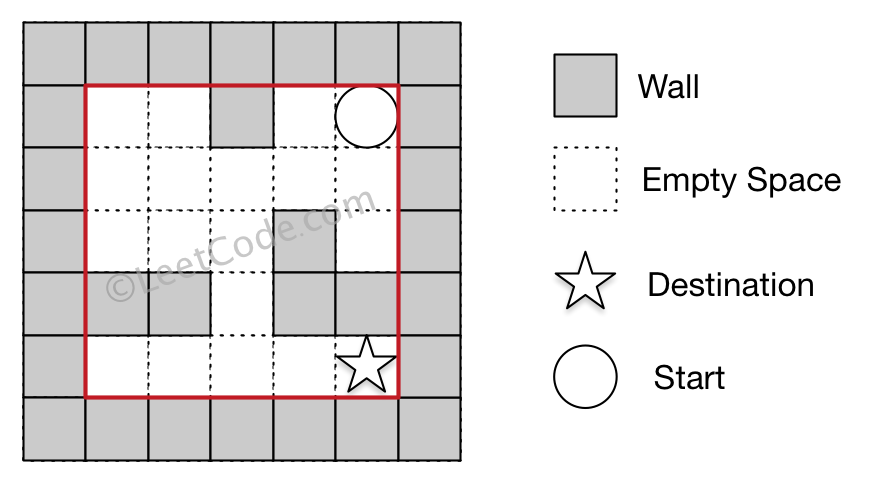
由空地和墙组成的迷宫中有一个球。球可以向上下左右四个方向滚动,但在遇到墙壁前不会停止滚动。当球停下时,可以选择下一个方向。
给定球的起始位置,目的地和迷宫,找出让球停在目的地的最短距离。距离的定义是球从起始位置(不包括)到目的地(包括)经过的空地个数。如果球无法停在目的地,返回 -1。
迷宫由一个0和1的二维数组表示。 1表示墙壁,0表示空地。你可以假定迷宫的边缘都是墙壁。起始位置和目的地的坐标通过行号和列号给出。
示例 1:
输入 1: 迷宫由以下二维数组表示
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
输入 2: 起始位置坐标 (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
输入 3: 目的地坐标 (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)
输出: 12
解析: 一条最短路径 : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right。
总距离为 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12。
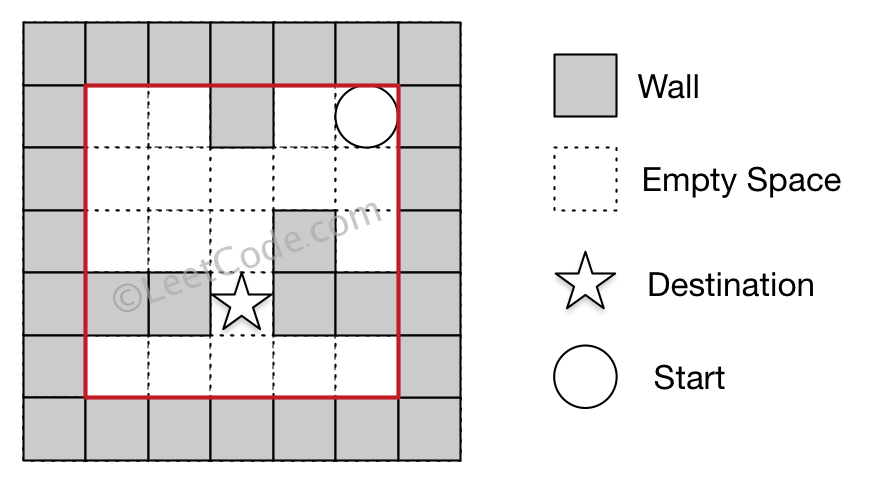
示例 2:
输入 1: 迷宫由以下二维数组表示 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 输入 2: 起始位置坐标 (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4) 输入 3: 目的地坐标 (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2) 输出: -1 解析: 没有能够使球停在目的地的路径。
注意:
- 迷宫中只有一个球和一个目的地。
- 球和目的地都在空地上,且初始时它们不在同一位置。
- 给定的迷宫不包括边界 (如图中的红色矩形), 但你可以假设迷宫的边缘都是墙壁。
- 迷宫至少包括2块空地,行数和列数均不超过100。
BFS。
注意在一般的广度优先搜索中,我们不会经过同一个节点超过一次,但在这道题目中,只要从起始位置到当前节点的步数 step 小于之前记录的最小步数 dist[i, j],我们就会把 (i, j) 再次加入队列中。
class Solution:
def shortestDistance(
self, maze: List[List[int]], start: List[int], destination: List[int]
) -> int:
m, n = len(maze), len(maze[0])
rs, cs = start
rd, cd = destination
dist = [[inf] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[rs][cs] = 0
q = deque([(rs, cs)])
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
x, y, step = i, j, dist[i][j]
while 0 <= x + a < m and 0 <= y + b < n and maze[x + a][y + b] == 0:
x, y, step = x + a, y + b, step + 1
if step < dist[x][y]:
dist[x][y] = step
q.append((x, y))
return -1 if dist[rd][cd] == inf else dist[rd][cd]class Solution {
public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int m = maze.length;
int n = maze[0].length;
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
dist[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i, y = j, step = dist[i][j];
int a = dirs[k], b = dirs[k + 1];
while (
x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] == 0) {
x += a;
y += b;
++step;
}
if (step < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = step;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
return dist[destination[0]][destination[1]] == Integer.MAX_VALUE
? -1
: dist[destination[0]][destination[1]];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size();
int n = maze[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dist(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
dist[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
queue<vector<int>> q {{start}};
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i, y = j, step = dist[i][j];
int a = dirs[k], b = dirs[k + 1];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < m && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n && maze[x + a][y + b] == 0) {
x += a;
y += b;
++step;
}
if (step < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = step;
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
return dist[destination[0]][destination[1]] == INT_MAX ? -1 : dist[destination[0]][destination[1]];
}
};func shortestDistance(maze [][]int, start []int, destination []int) int {
m, n := len(maze), len(maze[0])
dist := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = math.MaxInt32
}
}
dist[start[0]][start[1]] = 0
q := [][]int{start}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for len(q) > 0 {
i, j := q[0][0], q[0][1]
q = q[1:]
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y, step := i, j, dist[i][j]
a, b := dirs[k], dirs[k+1]
for x+a >= 0 && x+a < m && y+b >= 0 && y+b < n && maze[x+a][y+b] == 0 {
x, y, step = x+a, y+b, step+1
}
if step < dist[x][y] {
dist[x][y] = step
q = append(q, []int{x, y})
}
}
}
if dist[destination[0]][destination[1]] == math.MaxInt32 {
return -1
}
return dist[destination[0]][destination[1]]
}