You are given the strings key and message, which represent a cipher key and a secret message, respectively. The steps to decode message are as follows:
- Use the first appearance of all 26 lowercase English letters in
keyas the order of the substitution table. - Align the substitution table with the regular English alphabet.
- Each letter in
messageis then substituted using the table. - Spaces
' 'are transformed to themselves.
- For example, given
key = "happy boy"(actual key would have at least one instance of each letter in the alphabet), we have the partial substitution table of ('h' -> 'a','a' -> 'b','p' -> 'c','y' -> 'd','b' -> 'e','o' -> 'f').
Return the decoded message.
Example 1:
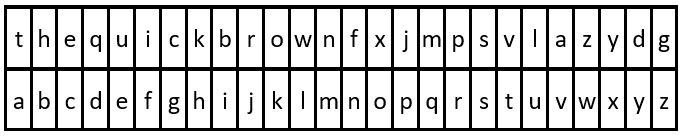
Input: key = "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog", message = "vkbs bs t suepuv" Output: "this is a secret" Explanation: The diagram above shows the substitution table. It is obtained by taking the first appearance of each letter in "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog".
Example 2:
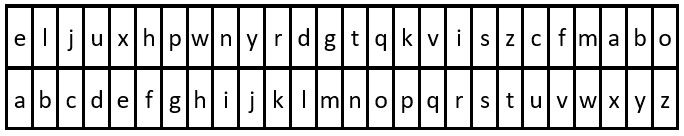
Input: key = "eljuxhpwnyrdgtqkviszcfmabo", message = "zwx hnfx lqantp mnoeius ycgk vcnjrdb" Output: "the five boxing wizards jump quickly" Explanation: The diagram above shows the substitution table. It is obtained by taking the first appearance of each letter in "eljuxhpwnyrdgtqkviszcfmabo".
Constraints:
26 <= key.length <= 2000keyconsists of lowercase English letters and' '.keycontains every letter in the English alphabet ('a'to'z') at least once.1 <= message.length <= 2000messageconsists of lowercase English letters and' '.
class Solution:
def decodeMessage(self, key: str, message: str) -> str:
d = {" ": " "}
i = 0
for c in key:
if c in d:
continue
d[c] = ascii_lowercase[i]
i += 1
return "".join(d[c] for c in message)class Solution {
public String decodeMessage(String key, String message) {
Map<Character, Character> d = new HashMap<>();
String lowcase = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
d.put(' ', ' ');
int i = 0;
for (char c : key.toCharArray()) {
if (d.containsKey(c)) {
continue;
}
d.put(c, lowcase.charAt(i++));
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : message.toCharArray()) {
ans.append(d.get(c));
}
return ans.toString();
}
}class Solution {
public:
string decodeMessage(string key, string message) {
unordered_map<char, char> d;
d[' '] = ' ';
int i = 0;
string lowcase = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
for (char c : key) {
if (d.count(c)) continue;
d[c] = lowcase[i]++;
}
string ans;
for (char c : message) ans.push_back(d[c]);
return ans;
}
};func decodeMessage(key string, message string) string {
d := map[rune]byte{}
d[' '] = ' '
i := 0
lowcase := "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
for _, c := range key {
if _, ok := d[c]; ok {
continue
}
d[c] = lowcase[i]
i++
}
var ans []byte
for _, c := range message {
ans = append(ans, d[c])
}
return string(ans)
}function decodeMessage(key: string, message: string): string {
let decodeMap = new Map();
const m = key.length,
n = 26;
for (let i = 0, j = 0; i < m; i++) {
let char = key.charAt(i);
if (char != ' ' && !decodeMap.has(char)) {
decodeMap.set(char, String.fromCharCode(j + 97));
j++;
}
}
let ans = [];
for (let char of message) {
ans.push(char == ' ' ? ' ' : decodeMap.get(char));
}
return ans.join('');
}