ng-loader is a loader for Webpack that can transform *.ng files into AngularJs Components.
Note: [email protected] had a different purpose than version 2.*, it was currently migrated to ng-module-loader.
webpack is a tool to build JavaScript modules in your application. To start using webpack from its cli or api, follow the Installation instructions.
webpack simplifies your workflow by quickly constructing a dependency graph of your application and bundling them in the right order. webpack can be configured to customise optimisations to your code, to split vendor/css/js code for production, run a development server that hot-reloads your code without page refresh and many such cool features. Learn more about why you should use webpack.
Loaders are transformations that are applied on a resource file of your application. They are functions (running in Node.js) that take the source of a resource file as the parameter and return the new source. Learn more about loaders.
npm install --save-dev ng-loader
Use the loader either via your Webpack config.
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.ng$/,
use: [ 'ng-loader' ]
}
]
}
}You can also configure ng-loader and the sub-loaders for your components. Bellow is the default configuration.
{
test: /\.ng$/,
use: [
{
loader: 'ng-loader'
options: {
hotReload: true,
loaders: {
html: [
'html-loader'
],
js: [
{
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['es2015'],
plugins: ['transform-runtime'],
comments: false
}
}
],
sass: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader'
]
}
}
}
]
}In AngularJS, a Component is a special kind of directive that uses a simpler configuration which is suitable for a component-based application structure.
This makes it easier to write an app in a way that's similar to using Web Components or using the new Angular's style of application architecture.
Advantages of Components:
- simpler configuration than plain directives
- promote sane defaults and best practices
- optimized for component-based architecture
- writing component directives will make it easier to upgrade to Angular
You can see the full documentation here.
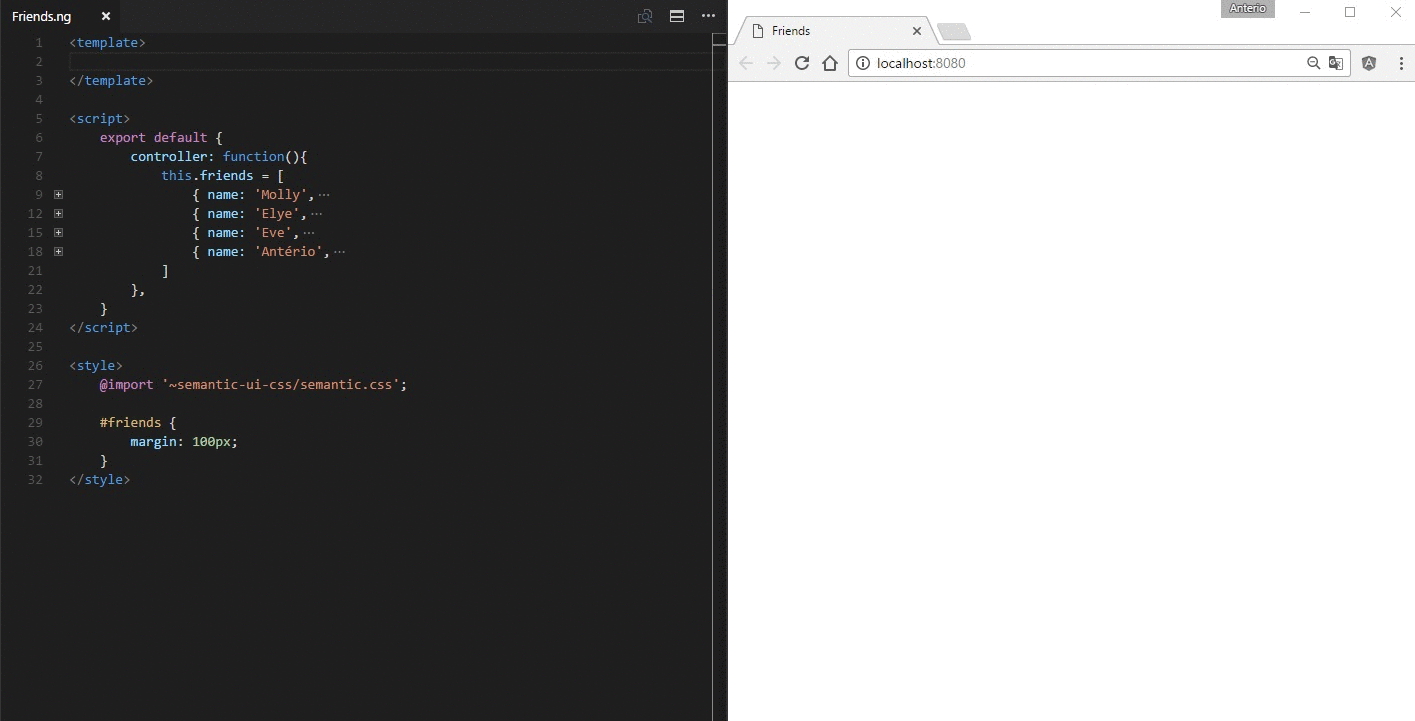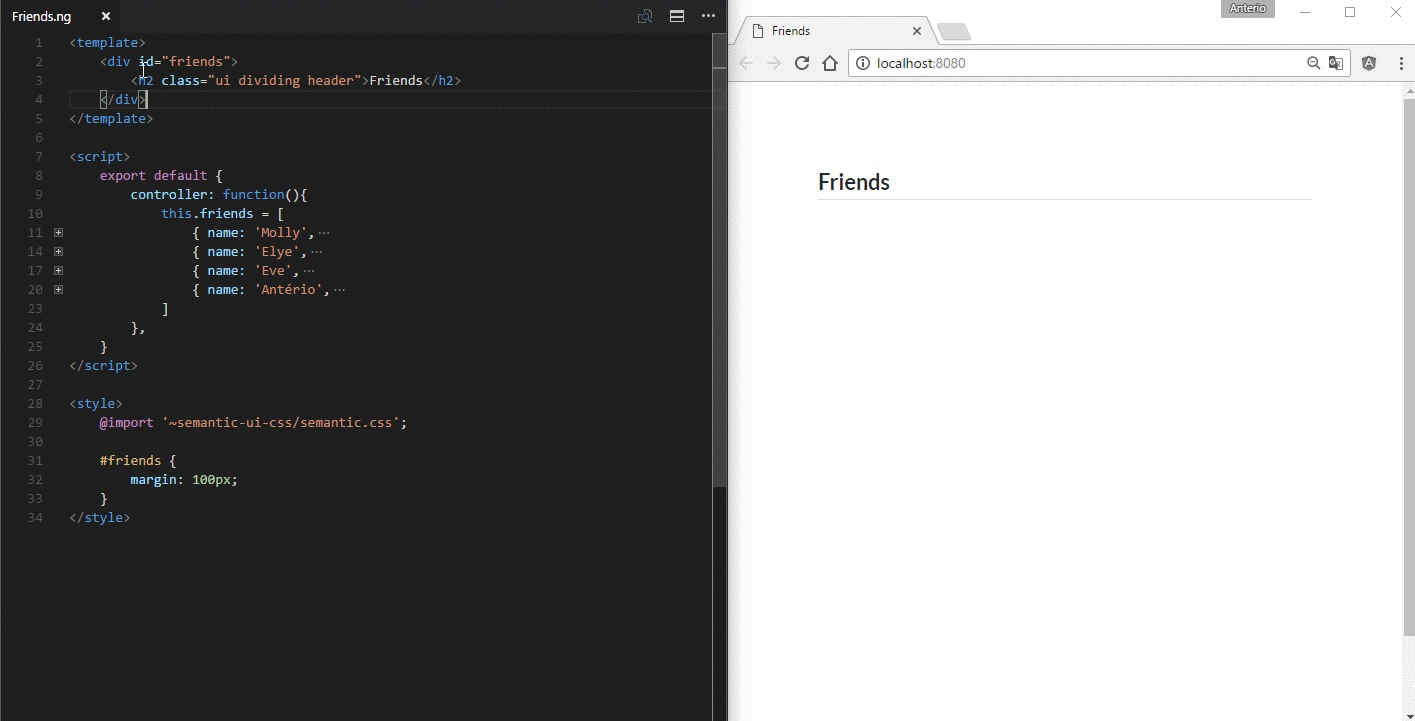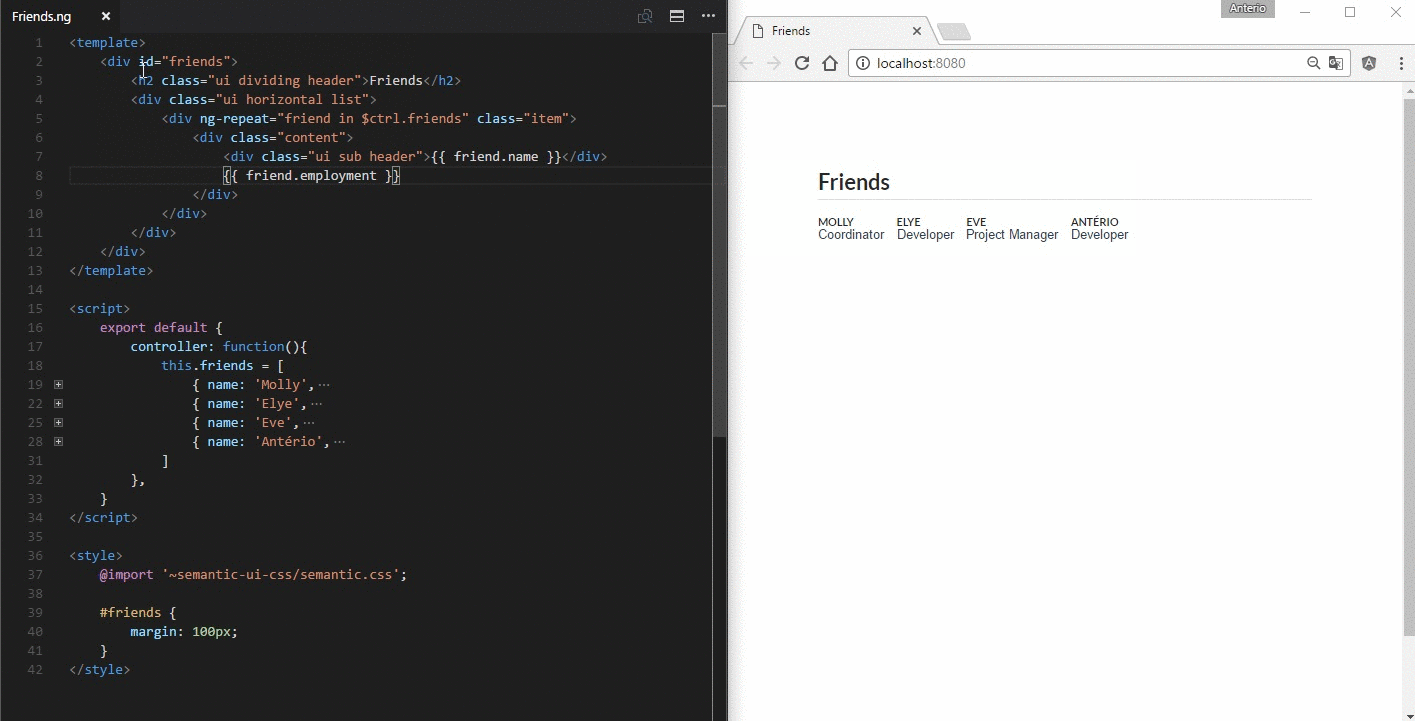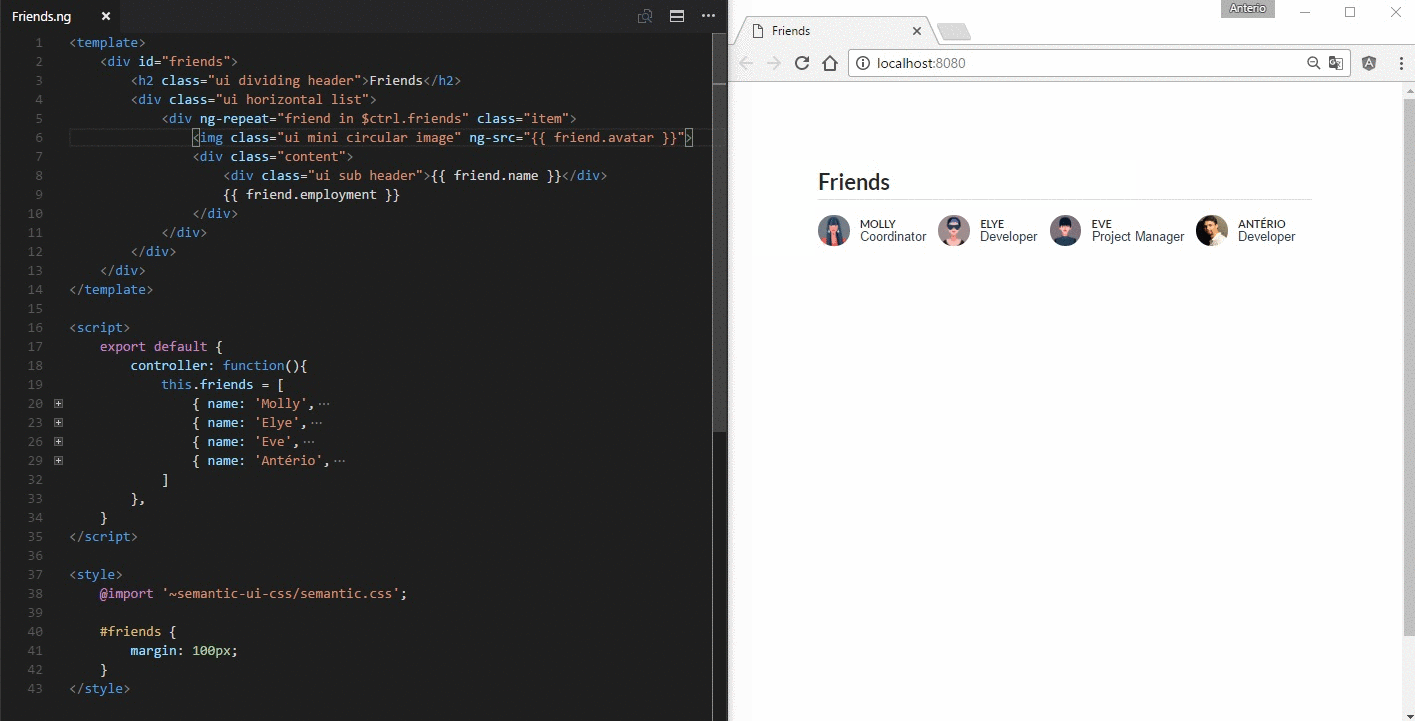
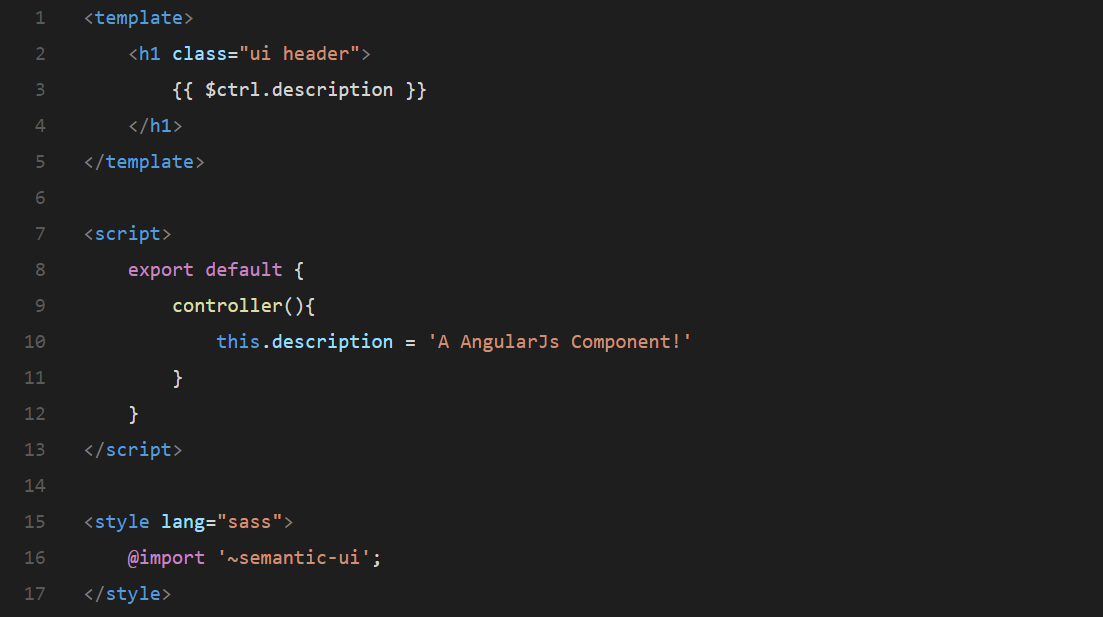
A *.ng file is a custom file format that uses HTML-like syntax to describe a angular component. Each *.ng file consists of three types of top-level language blocks: <template>, <script> and <style>:
<!-- ./src/components/my-component.ng -->
<template>
<h1 class="ui header">
{{ $ctrl.description }}
</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
controller(){
this.description = 'A AngularJs Component!'
}
}
</script>
<style lang="sass">
@import '~semantic-ui';
</style>ng-loader will parse the file, extract each language block, pipe them through other loaders if necessary, and finally assemble them back into a CommonJS module whose module.exports is a AngularJs Component options object.
-
Default language:
html. -
Each
*.ngfile can contain at most one<template>block at a time. -
Contents will be extracted as a string and used as the
templateoption for the compiled AngularJs Component.
-
Default language:
js(ES2015 is supported automatically ifbabel-loaderorbuble-loaderis detected). -
Each
*.ngfile can contain at most one<script>block at a time. -
The script is executed in a CommonJS like environment (just like a normal
.jsmodule bundled via Webpack), which means you canrequire()other dependencies. And with ES2015 support, you can also use theimportandexportsyntax.
// tag script inside ng file ./src/components/my-component.ng
exports default {
controller () {
this.description = 'A AngularJs Component';
}
};Registering your component:
import * as angular from 'angular';
import myComponent from './components/my-component.ng';
angular.module('app', []).component('myComponent', myComponent);You can also return an array with the component data. The first item represents the component name and the second component options.
// tag script inside ng file ./src/components/my-component.ng
exports default ['myComponent', {
controller: () => {
this.description = 'AngularJs';
}
}];and register as follows
import * as angular from 'angular';
import myComponent from './components/my-component.ng';
angular.module('app', []).component.apply(angular, myComponent);
// ES2015
// .component(...myComponent)- Default Language:
css; - Multiple
<style>tags are supported in a single*.ngfile; - By default, contents will be extracted and dynamically inserted into the document's
<head>as an actual<style>tag usingstyle-loader;
<my-component></my-component>This feature is provided by ng-hot-reload-api
You can treat *.ng files as HTML in your editor.