These scripts correspond to a (differential) ATAC-seq analysis workflow as described in our recent report. It is largely based on the pipeline developed by Anshul Kundaje's group (Stanford) and the ENCODE project.
If you use this methodology, please cite the following paper along with corresponding pipeline dependencies:
Jake J. Reske, Mike R. Wilson, and Ronald L. Chandler. 2020. ATAC-seq normalization method can significantly affect differential accessibility analysis and interpretation. Epigenetics & Chromatin 13: 22.
Attempt to run each command individually or in blocks after editing to match your own data architecture.
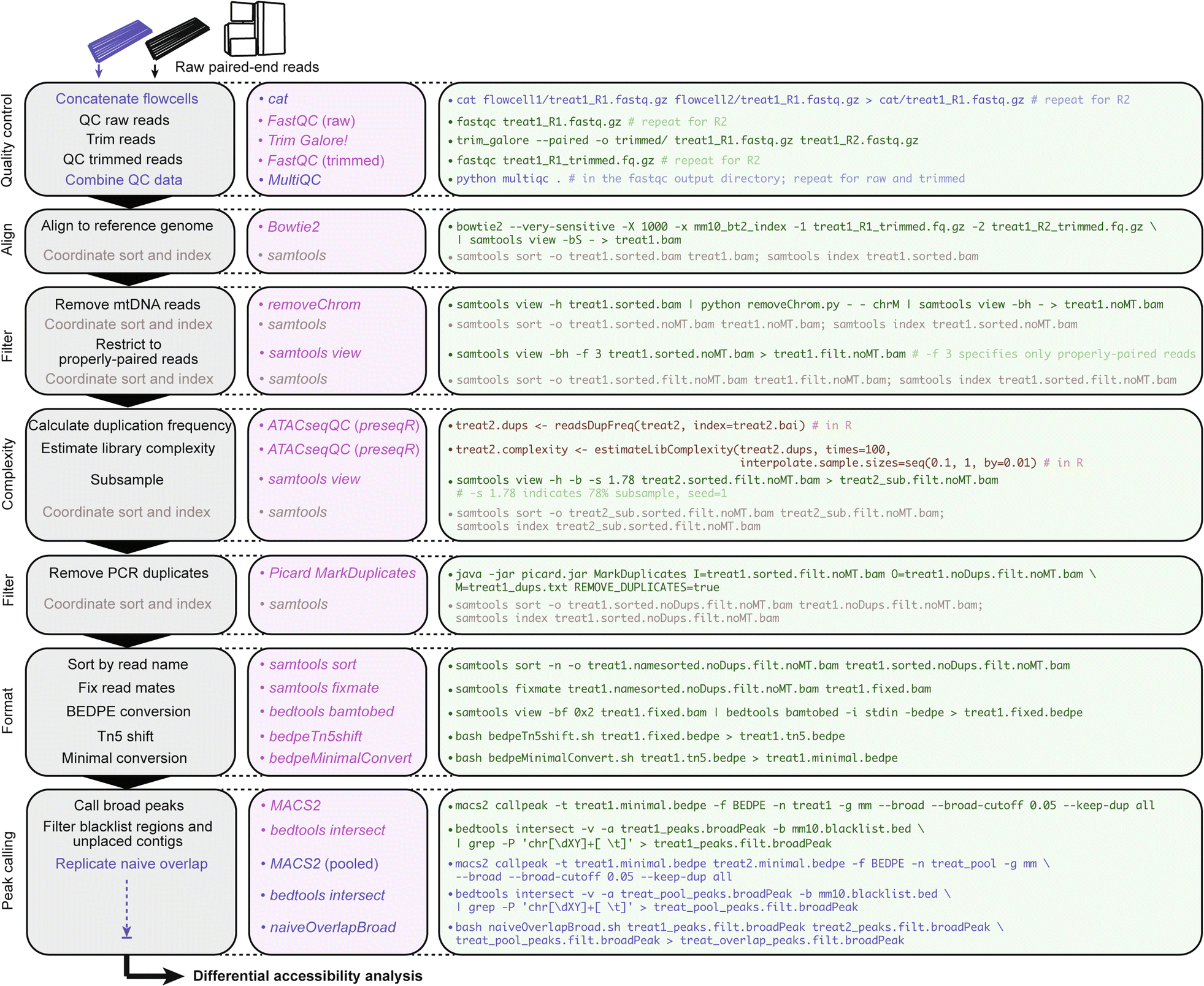
Generalized ATAC-seq data processing workflow intended for comparative analysis. Stepwise bioinformatics process and example commands for analyzing ATAC-seq data from raw reads to calling peaks for downstream differential accessibility analysis. Consider “treat1” as an example mouse ATAC-seq Illumina paired-end library. Blue text denotes optional or conditional steps dependent on experimental design and desired output. Users seeking only to discover replicate-concordant accessible regions in a singular cell state may wish to call naïve overlapping peaks, though this step is not necessary for differential accessibility analysis.
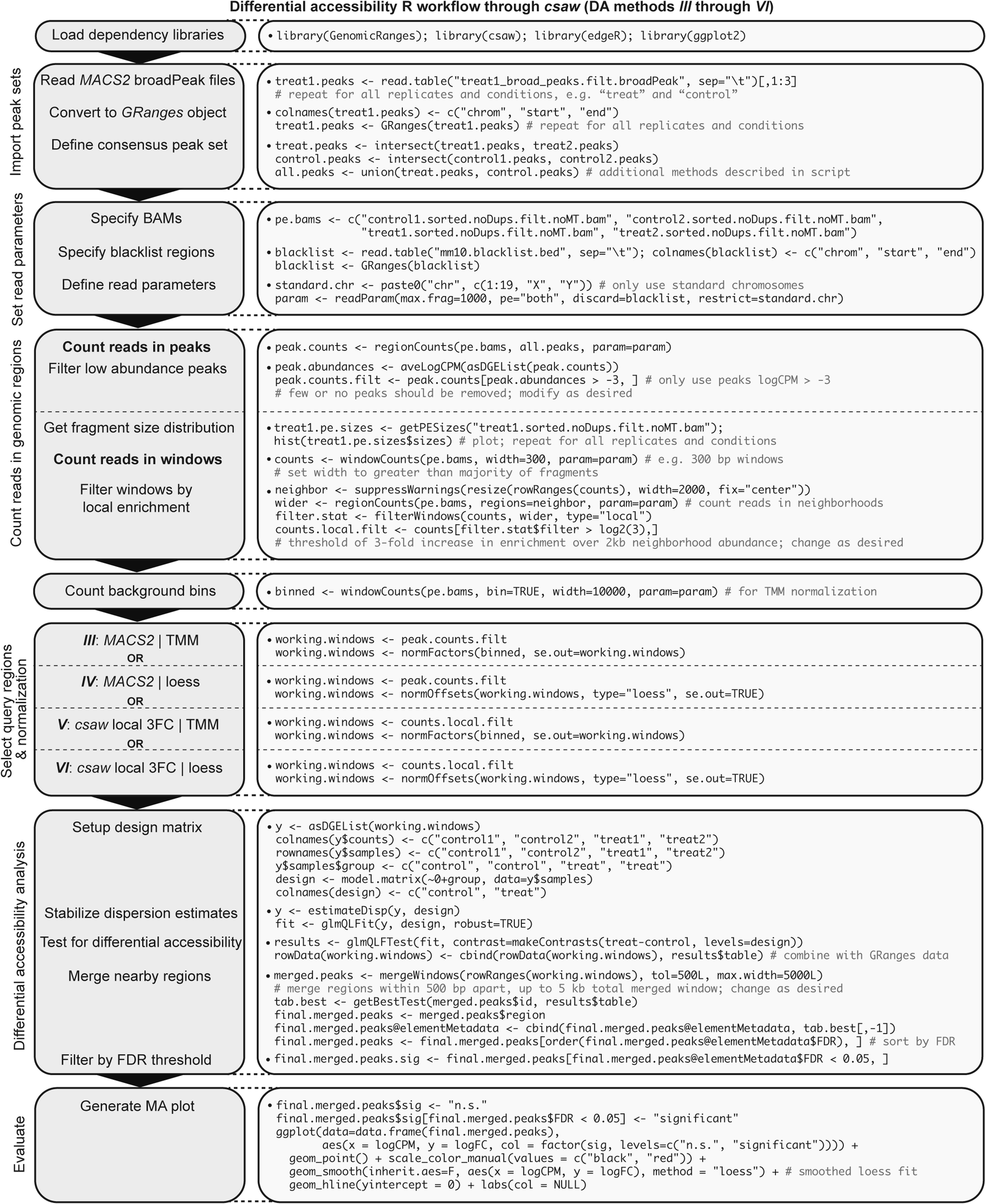
csaw workflow for multiple differential accessibility analyses in R. Consider an experimental design with n = 2 biological replicates from two conditions: “treat” and “control”. Describes implementation of two possible normalization methods and use of either MACS2 peaks or de novo locally enriched windows as query regions for output comparison; see csaw manual for additional normalization frameworks. Note: updates to the behavior of certain csaw functions have required slight compatibility changes to the commands described graphically, so please reference the latest R script.