| title | description |
|---|---|
Model tab |
The Model tab contains tools for manipulating 3D objects and models, working with physical constraints, and more. |
import BetaAlert from '../includes/beta-features/beta-alert.md'
The model tab contains tools for manipulating 3D objects in the workspace, creating detailed models, working with physical constraints, and adding advanced objects.
The primary transform tools include Select, Move, Scale, Rotate, and Transform. When you choose a tool, visual draggers display on the selected object in the 3D viewport.
Move Scale RotateTool transform snapping increments are based on studs for moving/scaling or degrees for rotating, each adjustable in the Model tab. While transforming, you can temporarily toggle snapping by holding the Shift key.
If the selected object and its visual draggers are not currently in view within the 3D viewport, you can press the Tab key to "summon" the draggers to your mouse pointer position, allowing you to transform the selected object from your current viewpoint.The Mode selector toggles between standard geometric transformations and simulation of mechanical constraints while moving or rotating parts.
The Collisions checkbox toggles the collisions state when you're transforming objects. If collisions are off, you can move, scale, and rotate objects so that they overlap each other; if collisions are on, you cannot transform objects to overlap other objects.
Snap increments for tool transforms are based on studs for moving/scaling or degrees for rotating. To enable or disable snapping:
-
Temporarily toggle snapping either on or off by holding Shift while transforming.
-
Toggle the checkbox next to Rotate or Move, and adjust the rotation/transform increments via the input fields.

CtrlL on Windows or ⌘L on Mac toggles between transforming an object relative to world coordinates or the object's local coordinates. When in local mode, an L symbol appears to the lower-right of the object.
The Pivot tools give you full control over the points around which objects rotate and translate. See Pivot Tools for details.
The Align Tool button opens a set of tools for aligning objects or groups of objects along the X, Y, or Z axes. For more information, see Align Tool.
The Part button inserts a new part into the workspace. Clicking the small dropdown arrow on the button lets you select either Block, Sphere, Wedge, Corner Wedge, or Cylinder. For more information, see Parts.
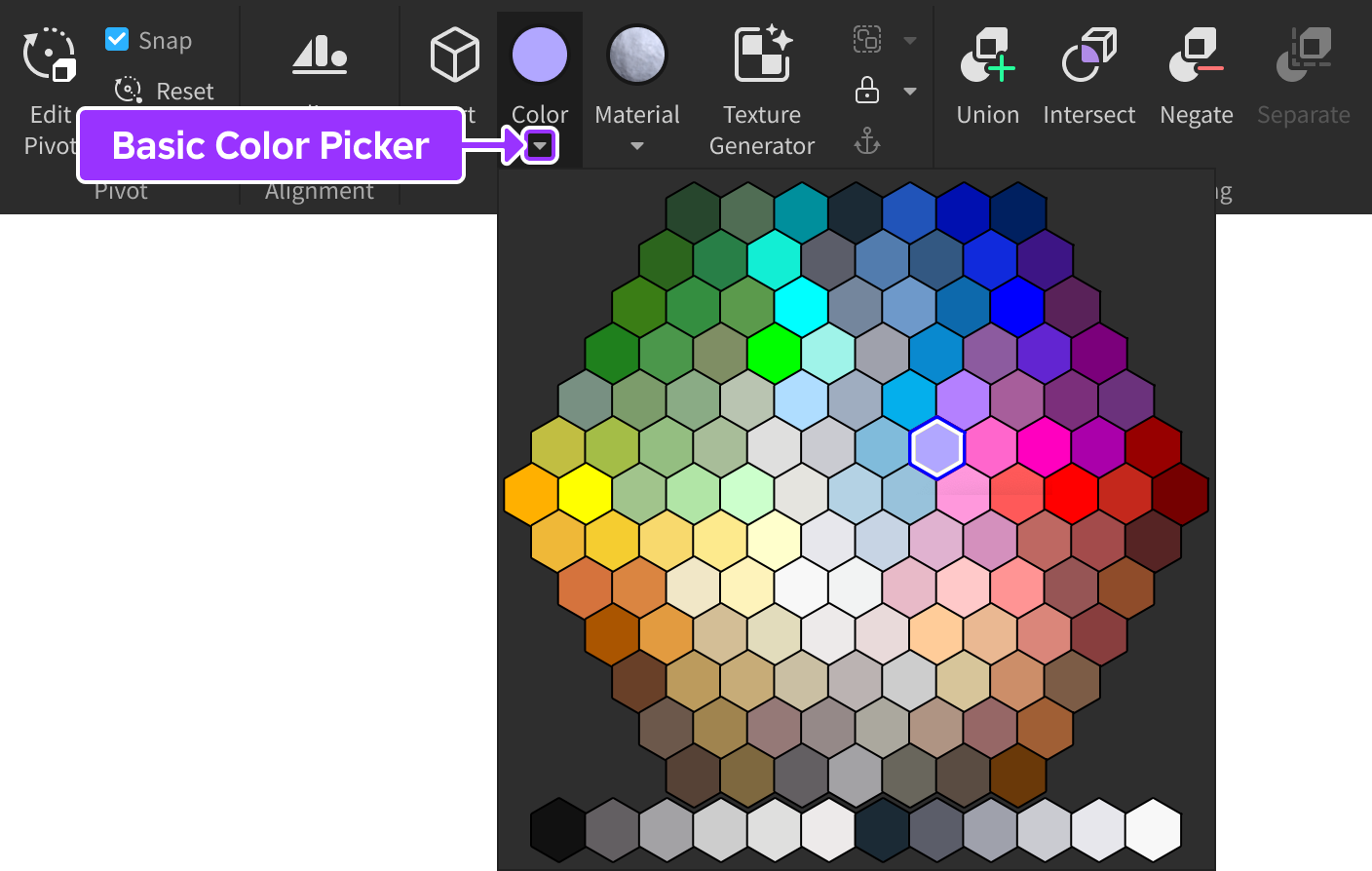
Clicking the small dropdown arrow on the Color widget reveals a hexagonal color picker.
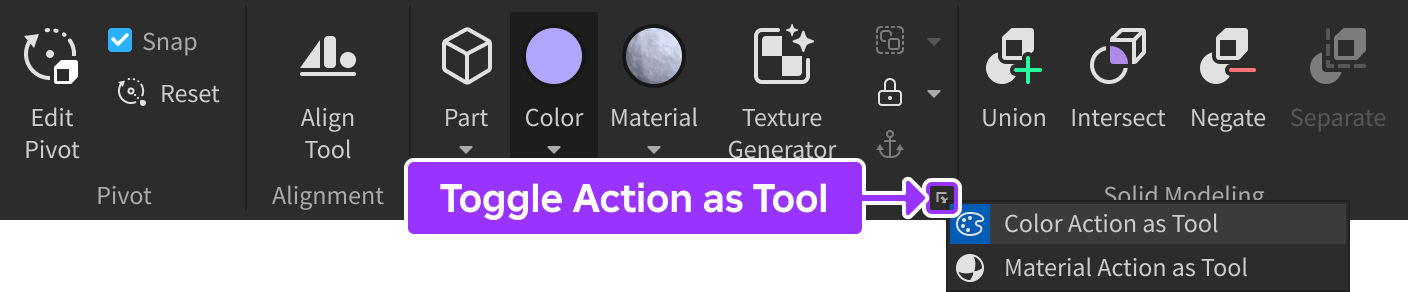
By default, clicking the overall Color button applies the chosen color to any selected parts. If you prefer a fill/paint workflow instead, toggle on Color Action as Tool and then click parts in the 3D viewport to apply the chosen color.
For alternative ways to apply custom colors, see [Coloring Parts](../parts/index.md#colors-popup).Clicking the small dropdown arrow on the Material widget reveals a material picker.
By default, clicking the overall Material button applies the chosen material to any selected parts. If you prefer a fill/paint workflow instead, toggle on Material Action as Tool and then click parts in the 3D viewport to apply the chosen material.
The Texture Generator tool quickly creates custom textures for meshes through text prompts.
You can group objects into a model by selecting them and clicking the Group button. This action has a default shortcut of CtrlG (Windows) or ⌘G (Mac).
Alternatively, you can group objects into a folder by clicking the small arrow next to the button and selecting Group as a Folder. This action has a default shortcut of AltCtrlG (Windows) or ⌥⌘G (Mac).
To ungroup an existing model or folder, click the small arrow next to the button and select Ungroup. This action has a default shortcut of CtrlU (Windows) or ⌘U (Mac).
You can enable the Lock Tool by clicking the small arrow next to the Lock button and selecting Lock Tool. This action has a default shortcut of AltL (Windows) or ⌥L (Mac).
Once enabled, the tool operates as a "key" for both states — clicking on an unlocked object locks it, while clicking a locked object unlocks it.
To unlock all objects, click the small arrow next to the button and select Unlock All.
The Anchor toggle controls whether the part will be immovable by physics. When Class.BasePart.Anchored|Anchored, a part will never change position due to gravity, other parts collisions, overlapping other parts, or any other physics-related causes. This action has a default shortcut of AltA (Windows) or ⌥A (Mac).
The Solid Modeling section contains tools to create new geometry beyond the basic parts Roblox provides. For more information, see Solid Modeling.
| Tool | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
| **Union** | ShiftCtrlG (Windows) Shift⌘G (Mac) |
Join two or more parts together to form a single solid union. |
| **Intersect** | ShiftCtrlI (Windows) Shift⌘I (Mac) |
Intersect overlapping parts into a single solid intersection. |
| **Negate** | ShiftCtrlN (Windows) Shift⌘N (Mac) |
Negate parts, useful for making holes and indentations. |
| **Separate** | ShiftCtrlU (Windows) Shift⌘U (Mac) |
Separate the union or intersection back into its individual parts. |
The Constraints section contains tools for creating physical Class.Constraint|Constraints between objects.
Constraints are categorized into two groups:
- Mechanical Constraints — Constraints in this group behave as mechanical connections, including hinges, springs, motors, and ropes.
- Mover Constraints — Constraints in this group apply force or torque to move one or more assemblies
The Gameplay section tools allow you to insert beautiful effects like lights and particle emitters, as well as quickly insert a Class.SpawnLocation into the 3D space.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| **Effects** | Creates a new light or effect within the workspace or the selected object. The dropdown lets you select which type of effect to create. |
| **Spawn** | Adds a `Class.SpawnLocation` for players to appear at when they join the experience. |
The Advanced section contains tools to insert advanced objects, services, and scripts, as well as configure collision filtering.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| **Insert Object** | Opens the Insert Object popup for quick insertion of objects. |
| **Model** | Allows you to import a `Class.Model` from a local file. |
| **Service** | Allows you to insert services which are not listed in the Explorer by default. |
| **Collision Groups** | Opens a window which lets you create and edit collision groups for physical [collision filtering](../workspace/collisions.md#collision-filtering). |
| **Run Script** | Runs a `Class.Script` located in a file on your local machine. |
| **Script** | Inserts a `Class.Script` into the selected `Class.Instance`. |
| **LocalScript** | Inserts a `Class.LocalScript` into the selected `Class.Instance`. |
| **ModuleScript** | Inserts a `Class.ModuleScript` into the selected `Class.Instance`. You can implement his type of script to reuse code across other scripts. |