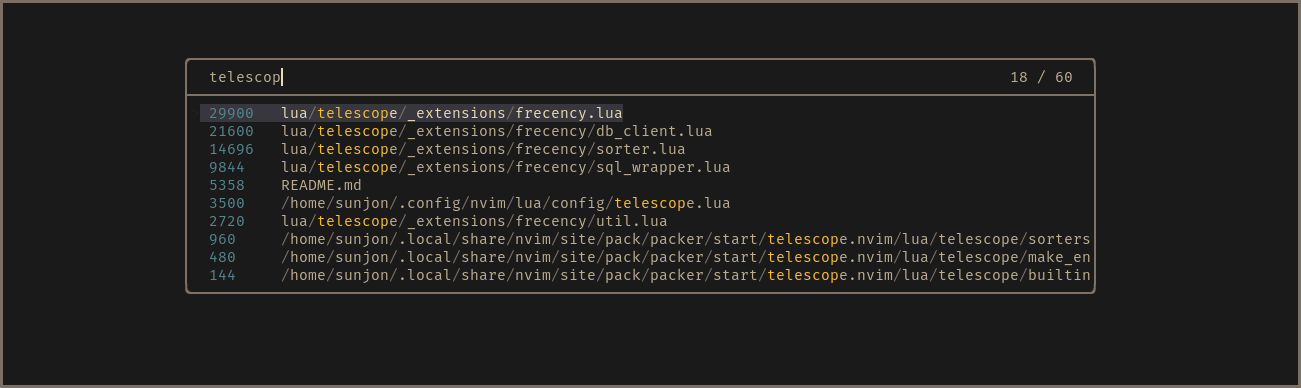
A telescope.nvim extension that offers intelligent prioritization when selecting files from your editing history.
Using an implementation of Mozilla's Frecency algorithm (used in Firefox's address bar), files edited frecently are given higher precedence in the list index.
As the extension learns your editing habits over time, the sorting of the list is dynamically altered to prioritize the files you're likely to need.
- Scores shown in finder for demonstration purposes - disabled by default
Frecency naturally works best for indexed files that have been given a reasonably high score.
New projects or rarely used files with generic names either don't get listed at all or can be buried under results with a higher score.
Frecency tackles this with Workspace Filters:
The workspace filter feature enables you to select from user defined filter
tags that map to a directory or collection of directories. Filters are applied
by entering :workspace_tag: anywhere in the query. You can complete names by
pressing <Tab> after the first : character (the case when
enable_prompt_mappings = true).
When a filter is applied, results are reduced to entries whose path is a descendant of the workspace directories. The indexed results are optionally augmented with a listing of all files found in a recursive search of the workspace directories. Non-indexed files are given a score of zero and appear below the frecent entries. When a non-indexed file is opened, it gains a score value and is available in future frecent search results.
In default, pre-defined workspace tag: CWD is available. that is, you can
filter entries into ones under the current working directory.
If the active buffer (prior to the finder being launched) is attached to an LSP
server, an automatic LSP tag is available, which maps to the workspace
directories provided by the language server.
- Neovim v0.10.0 or higher
- Use
^0.9.0tag for Neovim 0.9.x (See Notice for versioning).
- Use
- telescope.nvim (required)
- nvim-web-devicons (optional)
- fd or ripgrep (optional)
NOTE: fd or ripgrep will be used to list up workspace files. They are
extremely faster than the native Lua logic. If you don't have them, it
fallbacks to Lua code automatically.
This is an example for Lazy.nvim.
{
"nvim-telescope/telescope-frecency.nvim",
-- install the latest stable version
version = "*",
config = function()
require("telescope").load_extension "frecency"
end,
}See :h telescope-frecency-configuration to know about further configurations.
A tagged release 1.0.0 is published and it drops the support for Neovim 0.9.x.
If you are still using Neovim 0.9.x, use ^0.9.0 tag for your favorite plugin
manager.
{
"nvim-telescope/telescope-frecency.nvim",
-- install any compatible version of 0.9.x
version = "^0.9.0",
config = function()
require("telescope").load_extension "frecency"
end,
}:Telescope frecency
" Use a specific workspace tag:
:Telescope frecency workspace=CWD
" You can use with telescope's options
:Telescope frecency workspace=CWD path_display={"shorten"} theme=ivyFilter tags are applied by typing the :tag: name (adding surrounding colons)
in the finder query. Entering :<Tab> will trigger omni completion for
available tags (the case when enabled_prompt_mappings = true).
You can run unit tests included in this repository by a script.
# Run this in /path/to/telescope-frecency.nvim
bin/run-testsRun bin/run-tests -h for more details.