When conducting a supervised classification with deep learning, it is often recommended to work with a balanced classification dataset. Imbalanced data refers to a situation where the number of observations is not the same for all the classes in a classification dataset.
Deep learning network fail to cope with imbalanced training datasets as they are sensitive to the proportions of the different classes. As a consequence, it tends to favor the class with the largest proportion of observations (known as majority class), which may lead to misleading accuracies. This may be particularly problematic when we are interested in the correct classification of a “rare” class (also known as minority class).
This project addresses the issue of imbalanced image-classification datasets where some classes are under represented. This is done by generating new images for under represented classes through Generative Models.
The reference dataset being considered is German Traffic Sign Dataset and can be downloaded from the below link. (http://benchmark.ini.rub.de/?section=gtsrb&subsection=dataset).
Once downloaded, place train.p and test.p files (pickle format) in the “traffic-signs-data” folder.
List of Project files
- Traffic_Signs_GAN_train.py : Functionality included to train GAN.
- Traffic_Signs_GAN_evaluate.py : Functionality to use trained weights and then, to generate new images for the target class.
- Traffic-Signs-GAN.ipynb : This file is included as a quick reference for the flow of execution.
- Traffic-Signs-GAN.html : This file is again HTML version of Traffic-Signs-GAN.ipynb.
Steps to execute
Training
-
Command-line parameters to run Traffic_Signs_GAN_train.py [ iterations ] [ class_val ] [ goodrun_ref ]
- iterations: Number of iterations that the network should be trained for. Default = 14100
- class_val: Should be between 1 to 43. Default = 17
- goodrun_ref: There is also an option to restore weights from the previous good run. Weights should be availabe in the "weights/goodrun/" folder. Default = 12900
-
Run ‘python Traffic_Signs_GAN_train.py’ to train the Adversarial Network and to save trained weights. Real sample images from the dataset and generated images from the generator are saved after every 100 iterations in ‘images/train’ folder.
-
Periodically, check for the quality of generated images in 'images/training' folder. For any invalid generated images, try reducing learning rate of the discriminator / adversarial network.
Evaluation
-
Command-line parameters to run Traffic_Signs_GAN_evaluate.py [ class_val ] [ goodrun_eval ]
- class_val: Should be between 1 to 43. Default = 17
- goodrun_eval: Use weights from the previous good run and then, generate new images. Default = 13900
-
Run ‘python Traffic_Signs_GAN_evaluate.py’ to generate new images. These are saved in ‘images/evaluate’ folder.
MLFlow related commands
A few mlflow commands to try out.
mlflow run .
mlflow run . -P iterations=13100
mlflow run . -P iterations=13100 --no-conda
mlflow run . -e Traffic_Signs_GAN_train.py
mlflow run . -e Traffic_Signs_GAN_train.py --no-conda
mlflow run . -e Traffic_Signs_GAN_evaluate.py
mlflow run . -e Traffic_Signs_GAN_evaluate.py --no-conda
A few statistics about the dataset:
- Number of training examples = 39209
- Number of testing examples = 12630
- Image data shape = (32, 32, 3)
- Number of classes = 43
A few image samples from the training set are visualized below.
In the Training and Test samples distribution shown above the distribution of the data across 43 classes is significantly skewed. Frequency in classes [1 - 15] is very high. It is important to balance the distribution by generating image samples for those classes with less frequency.
This project demonstrates generating new sample images for Class = 17 (“No Entry” traffic sign).
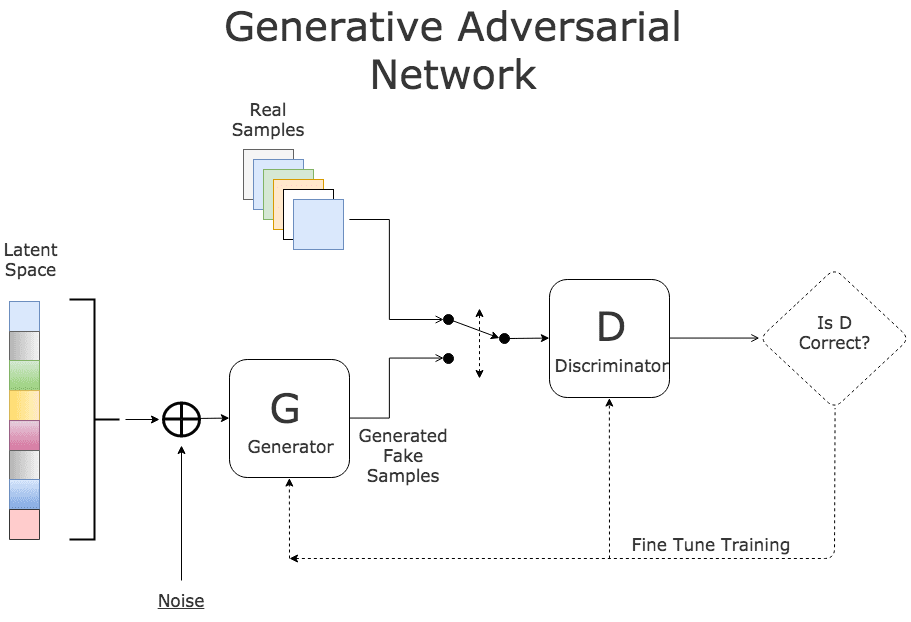
To generate new images, Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) model architecture has been adopted. This architecture involves two sub-models:
- A generator model for generating new examples.
Developing a generator model requires that we transform a vector from the latent space with, 100 dimensions to a 2D array with 32 × 32 × 3, or 3,072 values. There are a number of ways to achieve this, but there is one approach that has proven effective on deep convolutional generative adversarial networks.
- A discriminator model for classifying whether generated examples are real (from the domain) or fake (generated by the generator model).
The discriminator model must make predictions for the real and fake samples. The weights of the discriminator must be updated proportional to how correct or incorrect those predictions were.
- GAN Model is the third logical model subsuming Discriptive and Generative models.
Training Parameters
- Number of iterations: 14000
- Optimizer: Adam
- Training sample size per iteration: 1460
- Since available training sample size per epoch is small, Keras ImageDataGenerator has been used to augment data.
- No test set used since trained Generative Networks are expected to generate new images while taking random input from the latent space.
- Generalization:
- Data augmentation
- Drop-out
Including below, a few images generated at the end of training.
The generator model is responsible for creating new, fake, but plausible small photographs of objects. It does this by taking a point from the latent space as input and outputting a square color image.
From the below images, we can see that trained Generator has done a good job of generating new images that are very close to real sample images.
-
kdnuggets.com :
https://www.kdnuggets.com/2017/01/generative-adversarial-networks-hot-topic-machine-learning.html
-
machinelearningmastery.com
-
Book: Deep Learning with Python-Manning (2017) - François Chollet