-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
AutotestServerInstall
We have developed a script to automate the steps described below on a Ubuntu 12.04/12.10 server. So if you want to save yourself some time, please check the Installing Server/Scheduler/WebUI notes.
If you want to do it all yourself, we opted by keeping the documentation herem and we'll do the best to update it. However, we're always working on streamlining this process, so it might be possible that this can get out of sync.
If you find any step that might be outdated, please let us know, and we'll fix it.
We have automated this step on recent Ubuntu (12.04/12.10), although it should work on Debian too:
sudo /usr/local/autotest/installation_support/autotest-install-packages-deps
If you want to install it manually here it goes. Keep in mind this can be outdated, if so we kindly ask your help with keeping it up to date.
Install utility packages:
apt-get install -y unzip wget gnuplot makepasswd
Install webserver related packages (and Django):
apt-get install -y apache2-mpm-prefork libapache2-mod-wsgi python-django
Install database related packages:
apt-get install -y mysql-server python-mysqldb
Install java in order to compile the web interface, and git for cloning the autotest source code repository:
apt-get install git openjdk-7-jre-headless
Also, you'll need to install a bunch of auxiliary external packages
apt-get install python-imaging python-crypto python-paramiko python-httplib2 python-numpy python-matplotlib python-setuptools python-simplejson
Important: For this entire documentation, we will assume that you'll install autotest under /usr/local/autotest. If you use a different path, please change /usr/local/autotest accordingly. Please that you may have some issues with apache configuration if you don't choose /usr/local/autotest.
Important: We will also assume that you have created an autotest user on your box, that you'll use to perform most of the instructions after the point you have created it. Most of the instructions will use autotest unless otherwise noted.
As root:
useradd autotest passwd autotest [type in new password]
You can then clone the autotest repo (as root):
cd /usr/local git clone --recursive git://github.com/autotest/autotest.git chown -R autotest:autotest autotest
Log out, re-log as autotest, and then proceed.
Please check the shared Configuring Autotest Server Database notes
Run the build script to install necessary external packages. If you ran the package install script, you should have all you could get from your system packages and it would download only GWT. As autotest:
/usr/local/autotest/utils/build_externals.py
Always re-run this after a git pull if you notice it has changed, new dependencies may have been added. This is safe to rerun as many times as you want. It will only fetch and build what it doesn't already have. It's important to note that the autotest scheduler will also try to run build_externals.py whenever it's executed in order to make sure every piece of software has the right versions.
NOTE: Set the HTTP_PROXY environment variable to http://proxy:3128/ before running the above if your site requires a proxy to fetch urls.
If the only thing you want to do with Apache is run Autotest, you can use the premade Apache conf:
Ubuntu 12.04
sudo rm /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/mods-available/version.load /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/ sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/conf /etc/apache2/autotest.d sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/apache-conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/001-autotest sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/apache-web-conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/002-autotest
Ubuntu 12.10 - The version plugin now is compiled into apache, so it can't be enabled, otherwise you will have trouble.
sudo rm /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/conf /etc/apache2/autotest.d sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/apache-conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/001-autotest sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/apache-web-conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/002-autotest
You will have to comment the line
WSGISocketPrefix run/wsgi
In /usr/local/autotest/apache/conf/django-directives, as we found out that WSGI configuration varies among distros, and the version shipped with Ubuntu 12.04 is not compatible with this directive.
Also, you'll need to enable rewrite mod rules, which you can do by
a2enmod rewrite
Then, update your apache2 service
update-rc.d apache2 defaults
If you want to do other things on the Apache server as well, you'll
need to insert the following line into your Apache conf, under the
appropriate VirtualHost section:
Include "/usr/local/autotest/apache/apache-conf" Include "/usr/local/autotest/apache/apache-web-conf"
And make sure the rewrite mod is enabled, as well as the autotest config file directory is properly linked:
sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/mods-available/version.load /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/ sudo ln -s /usr/local/autotest/apache/conf /etc/apache2/autotest.d
Note: You will have to enable mod_env on SuSE based distro's for the all-directives to load properly when apache is started.
Important: Edit the following files to match the database passwords you set earlier during session #Set_up_MySQL, as autotest, more specifically, MYSQL_AUTOTEST_PASS.
/usr/local/autotest/global_config.ini /usr/local/autotest/shadow_config.ini
Important: Please, do not change this field
[AUTOTEST_WEB] # Machine that hosts the database host: localhost
As we are doing the setup on the same machine where mysql is running, so please, pretty please don't change it otherwise you will have trouble moving forward.
Things that you usually want to change on global_config.ini:
Section AUTOTEST_WEB
# DB password. You must set a different password than the default password: please_set_this_password
Section SCHEDULER
# Where to send emails with scheduler failures to # (usually an administrator of the autotest setup) notify_email: # Where the emails seem to come from (usually a noreply bogus address) notify_email_from:
Section SERVER
# Use custom SMTP server # If none provided, will try to use MTA installed on the box smtp_server: # Use custom SMTP server # If none provided, will use the default SMTP port smtp_port: # Use custom SMTP user # If none provided, no authentication will be used smtp_user: # Use SMTP password # It only makes sense if SMTP user is set smtp_password:
Important: If you set up your database using autotest-database-turnkey, this step can be safely skipped.
During the time span of the project, the autotest database went through design changes. In order to make it able for people running older versions to upgrade their databases, we have the concept of migration. Migration is nothing but starting from the initial database design until the latest one used by this specific version of the application. As autotest:
/usr/local/autotest/database/migrate.py --database=AUTOTEST_WEB sync
Important: If you set up your database using autotest-database-turnkey, this step can be safely skipped.
You have to run syncdb twice, due to peculiarities of the way syncdb works on Django. As autotest:
/usr/local/autotest/frontend/manage.py syncdb /usr/local/autotest/frontend/manage.py syncdb
Compile the Autotest web application and TKO frontend. As autotest:
/usr/local/autotest/utils/compile_gwt_clients.py -a
You will need to re-compile after any changes/syncs of the frontend/client pages.
Make everything in the /usr/local/autotest directory
world-readable, for Apache's sake:
chmod -R o+r /usr/local/autotest find /usr/local/autotest/ -type d | xargs chmod o+x chmod o+x /usr/local/autotest/tko/*.cgi
sudo apache2ctl restart
You should be able to access the web frontend at http://localhost/afe/, or http://your.server.fully.qualified.name.or.ip/afe/
To start the scheduler on reboot, you can setup init.d.
sudo cp /usr/local/autotest/utils/autotest.init /etc/init.d/autotestd sudo update-rc.d /etc/init.d/autotestd defaults
Then, you can reboot and you will see autotest-scheduler-watcher and autotest-scheduler processess running.
If you're using systemd, we ship a systemd service file. Copy the service file to systemd service directory. As root or using sudo:
sudo cp /usr/local/autotest/utils/autotestd.service /etc/systemd/system/
Make systemd aware of it:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Start the service:
sudo systemctl start autotestd.service
Check its status:
autotestd.service - Autotest scheduler
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/autotestd.service)
Active: active (running) since Wed, 25 May 2011 16:13:31 -0300; 57s ago
Main PID: 1962 (autotest-schedu)
CGroup: name=systemd:/system/autotestd.service
├ 1962 /usr/bin/python -u /usr/local/autotest/scheduler/autotest-scheduler-watcher
└ 1963 /usr/bin/python -u /usr/local/autotest/scheduler/autotest-scheduler /usr/local/autotest/results
You can execute the babysitter scripter through, let's say, nohup or screen. It is important to remember that by design, it's better to create an 'autotest' user that can run the scheduler and communicate with the machines through ssh. As root:
yum install screen
As autotest:
screen /usr/local/autotest/scheduler/autotest-scheduler-watcher
You can even close the terminal window with screen running, it will keep the babysitter process alive. In order to troubleshoot problems, you can pick up the log file that autotest-scheduler-watcher prints and follow it with tail. This way you might know what happened with a particular scheduler instance.
Clients are managed in the tab hosts of the web frontend. It is important that you can log onto your clients from your server using ssh without requiring a password.
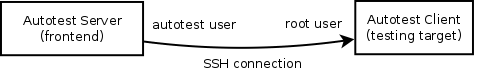
As autotest, on the server, create a RSA key in the following way:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Then, still on the server, and as autotest, copy it to the host:
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
You can import all the available tests inside the autotest client dir by running the test importer script as autotest:
/usr/local/autotest/utils/test_importer.py -A
If you did clone the autotest repo with --recursive, the virt test will be among the imported tests.
You can refer to the Autotest Troubleshooting Documentation documentation for some commonly reported problems and their root causes.
Please refer to the shared Autotest Virt Documentation
- The Parser is used to import results into TKO
- The Web Frontend Docs talks about using the frontend
- The Web Frontend Development Docs talks about setting up for frontend development work - you do not want to develop through Apache!